Reference no: EM13774930
Question 1: A relational database stores data in the form of:
lists.
forms.
columns.
tables.
spreadsheets.
Question 2: SQL stands for:
Standard Query Language.
Structural Question Language.
Structured Query Language.
Standard Question Language.
Structured Question Language.
Question 3: Which of the following is not a basic component of a database system?
Database
User
ERD
DBMS
Data applications
Question 4: A relational database is:
a self-describing collection of related tables.
a collection of forms and reports that support a given purpose.
a library of queries and data files for querying.
a set of applications and the data sets for those applications.
a set of metadata.
Question 5: Which of the following terms is synonymous with "tuple"?
Attribute
Table
Field
Row
Relation
Question 6: Which of the following terms is synonymous with "relation"?
Attribute
Table
Record
Row
Question 7: A primary key is:
required to be unique.
used to represent rows in relationships.
a candidate key.
used to identify unique rows.
All of these
Question 8: A candidate key is:
required to be unique.
used to represent rows in relationships.
a candidate to be the primary key.
Both required to be unique and used to represent rows in relationships
Both required to be unique and a candidate to be the primary key
Question 9: When the primary key of one relation is placed into a second relation, it is called a:
field key.
referential integrity.
foreign key.
candidate key.
relocated key.
Question 10: STUDENT (SID, StudentName, Major, AdvisorID)ADVISOR (AdvisorID, AdvisorName, Ofce, Phone)Given the relations above such that each student is assigned to one advisor, which of the following is true?
SID is both a primary key and a foreign key.
AdvisorName is a determinant.
AdvisorID is a foreign key.
Phone is a candidate key.
Major is a candidate key.
Question 11: One important relational design principle is that:
every determinant must be a candidate key.
every candidate key must not be a determinant.
every primary key must be a surrogate key.
every determinant must be functionally dependent on the primary key.
every primary key must be functionally dependent on every determinant.
Question 12: The first step of the normalization process is to:
identify all the candidate keys of a relation.
identify all the foreign keys of a relation.
identify all the functional dependencies of a relation.
identify all the determinants of a relation.
split the relation into two or more new relations.
Question 13: Which of the following is not true about primary keys?
Primary keys cannot be null.
Primary keys must be unique.
Primary keys must be a single attribute.
Primary keys are used to represent relationships.
Primary keys can be defined using a SQL CONSTRAINT phrase
Question 14: Which SQL keyword is used to specify a condition that rows must meet to be included in the results of an SQL SELECT query?
SELECT
FROM
WHERE
ORDER BY
GROUP BY
Question 15: Given the table CUSTOMER(CustID, Name, PhoneNum, AcctBalance), what is the standard SQL query phrase to retrieve the Name and Phone Number of customers?
SELECT CUSTOMER-Name AND CUSTOMER-PhoneNum
SELECT (CUSTOMER-Name AND CUSTOMER-PhoneNum)
SELECT Name, PhoneNum
SELECT (Name, PhoneNum)
SELECT *
Question 16: Given the table CUSTOMER(CustID, Name, PhoneNum, AcctBalance), what is the standard SQL query phrase to retrieve data for customers with an account balance greater than 50?
WHERE CUSTOMER-AcctBalance > 50
WHERE (CUSTOMER-AcctBalance > 50)
WHERE AcctBalance > 50
WHERE (AcctBalance > 50)
HAVING AcctBalance > 50
Question 17: Which of the following SQL commands would be used to remove only the data from a table named STUDENT while leaving the table structure intact?
DROP TABLE STUDENT;
DELETE TABLE STUDENT;
REMOVE TABLE STUDENT;
SELECT * FROM STUDENT THEN DROP;
DELETE FROM STUDENT;
Question 18: Which of the following SQL commands would be used to remove both the data and the table structure of a table named STUDENT?
DROP TABLE STUDENT;
DELETE TABLE STUDENT;
REMOVE TABLE STUDENT;
SELECT * FROM STUDENT THEN DROP;
DELETE FROM STUDENT;
Question 19: A dashed line between entities indicates:
a unique identifier.
a minimum cardinality of zero.
a minimum cardinality of one.
an identifying relationship.
a nonidentifying relationship.
Question 20: In crow's foot style E-R diagrams, a circle across the relationship line near an entity indicates:
a minimum cardinality of zero.
a minimum cardinality of one.
a maximum cardinality of one.
a maximum cardinality of many.
Both a minimum cardinality of one and a maximum cardinality of one
Question 21: In crow's foot style E-R diagrams, a crow's foot mark on the relationship line near an entity indicates:
a minimum cardinality of zero.
a minimum cardinality of one.
a maximum cardinality of one.
a maximum cardinality of many.
Both a minimum cardinality of one and a maximum cardinality of one
Question 22: Which of the following would be a reason to denormalize a relation?
Relax security
Lack of design time
End user preference
Improve performance
None of these
Question 23: Which of the following is true about representing a weak entity with the relational model?
If the weak entity is existence-dependent, the key of the parent must be part of the key of the weak entity.
If the strong entity has a minimum cardinality of 1, the key of the weak entity must be part of the strong entity.
If the weak entity is ID-dependent, the key of the weak entity must be part of the key of the parent entity.
If the weak entity is ID-dependent, the key of the parent entity must be part of the key of the weak entity.
If the parent entity is existence-dependent, then the minimum cardinality of the weak entity is zero.
Question 24: Which normal form was developed in order to eliminate multivalued dependencies?
3NF
BCNF
4NF
5NF
DK/NF
Question 25: The fundamental rule of normalization can be stated as:
every table must meet the definition of a relation.
every determinant must be a candidate key.
every domain must be logical consequence of the constraints.
every key must be a candidate key.
every constraint must be a determinant.
Question 26: Given the generic relation: GENERIC (PKey1, PKey2, Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3), and the functional dependencies: (PKey1, PKey2) → Attribute1 and PKey2 → (Attribute2, Attribute3), which of the following is true?
GENERIC is not fully normalized.
PKey1 is a determinant.
PKey2 is a candidate key.
GENERIC is in DK/NF.
All of these
Question 27: Given TABLE_A (Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3) and TABLE_B (Attribute4, Attribute5, Attribute6) shown in the figure below, which of the following would display the correct placement of foreign keys in the relational model?
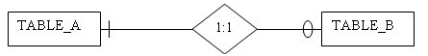
TABLE_A (Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3)TABLE _B (Attribute4, Attribute5, Attribute6, Attribute1)
TABLE _A (Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3, Attribute4, Attribute5)TABLE _B (Attribute4, Attribute5, Attribute6)
TABLE _A (Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3, Attribute4)TABLE _B (Attribute4, Attribute5, Attribute6, Attribute1)
TABLE _A (Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3)TABLE _B (Attribute4, Attribute5, Attribute6)
TABLE _A (Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3, Attribute6)TABLE _B (Attribute4, Attribute5, Attribute6)
Question 28: Which of the following is the correct technique for representing a 1:N relationship in the relational model?
The key of the entity on the one side is placed into the relation for the entity on the many side.
The key of the child is placed into the relation of the parent.
The key of either relation can be placed into the other relation.
The key of the entity on the many side is placed into the relation for the entity on the one side.
An intersection relation is created and the keys from both parent entities are placed as keys in the intersection relation.
Question 29: Given the entities PRODUCT and SUPPLIER shown in the figure below, which of the following would represent the correct placement of foreign keys?
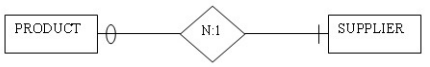
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber, ProductID)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost, SupplierID)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber, ProductID)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost, ContactName)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost, SupplierID)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber)
Question 30: Given the PRODUCT and SUPPLIER entities in the figure below, which of the following would represent the correct placement of foreign keys?

PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost, SupplierID)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber, ProductID)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber)PRODUCT_SUPPLIER (ProductID, SupplierID)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost, SupplierID)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber)
PRODUCT (ProductID, Description, Cost)SUPPLIER (SupplierID, ContactName, PhoneNumber)PRODUCT_SUPPLIER (ProductID, SupplierID
Question 31: What relationship pattern is illustrated in the following schema?
VEHICLE (VehicleID, Cost)
CAR (VehicleID, NumberOfSeats)
TRUCK(VehicleID, CargoCapacity)
VehicleID in CAR must exist in VehicleID in VEHICLE
VehicleID in TRUCK must exist in VehicleID in VEHICLE
Association relationship
Intersection relationship
Recursive relationship
Strong entity relationship
Supertype/subtype relationship
Question 32: The purpose of concurrency control is to:
ensure that each form has a corresponding report.
ensure that ASPs do not duplicate JSPs.
ensure that one user's work does not interfere with another's.
ensure that stored procedures do not invoke triggers.
ensure that triggers do not invoke stored procedures.
Question 33: When a transaction functions in such a way that either all of the transaction actions are completed or none of them will be, the transaction is said to be:
consistent.
isolated.
atomic.
locked.
logical.
Question 34: What concurrent processing problem occurs when a transaction reads a changed record that has not been committed to the database?
Nonrepeatable reads
Phantom reads
Dirty reads
Serialized reads
Unlocked reads
Question 35: Preventing multiple applications from obtaining copies of the same record when the record is about to changed is called:
serialized reading.
lost updating.
concurrent processing.
resource locking.
block factoring.
Question 36: Which of the following is not true of database recovery through reprocessing?
Reprocessing makes use of a database save.
Reprocessing takes the same amount of time as did processing in the first place.
Reprocessing will always return the database to its exact previous state.
Reprocessing requires a record of all transactions since the last time the database was saved.
All of these are true of reprocessing.
Question 37: ODBC stands for:
Open Database Compatibility.
Open Database Connectivity.
Open-source Database Compatibility.
Open-source Database Connectivity.
None of these
Question 38: If the computer hosting the Web server is running a Unix or Linux operating system, the Web server is probably:
Apache.
Tomcat.
Internet Information Server (IIS).
Internet Interpreter Server (IIS).
Information Interpreter Server (IIS).
Question 39: In PHP, any programming language statements that are to be processed on the server must be enclosed in:
<!-- and --!>.
[php and php].
(php and php).
<?php and ?>.
<server> and </server>.
Question 40: The final step of using a PHP connection to a DBMS is to open the connection.
test the connection.
query the database.
process the query results.
close the connection.
Question 41: XML document s can be ________ against their XML Schema.
measured
grown
validated
browsed
All of these
Question 42: XML Schemas consist of ________.
elements
attributes
properties
Both elements and attributes
All of these
Question 43: When working with Microsoft Access on a Windows operating system, a simple but usable ASCII text editor is:
Microsoft Word.
Notepad.
Wordpad.
Microsoft Frontpage.
Microsoft Visual Studio .NET.
Question 44: Business Intelligence (BI) systems do which of the following?
Analyze current and past activities
Predict future events
Record and process transactions
Both Analyze current and past activities and Predict future events
All of these
Question 45: Data mining applications are used accomplish which of the following tasks?
Perform what-if analysis
Make predications
Facilitate decision making
Both Perform what-if analysis and Make predications
All of these
Question 46: We have obtained access to the company's operational data. In one record, we find that a customer's age has been recorded as "337". This is an example of:
dirty data.
inconsistent data.
non-integrated data.
a "wrong format" problem.
a "too much data" problem.
Question 47: We have obtained access to the company's operational data. We examine 50 records for customers with phone numbers that should use the current area code of 345. Of these 50 records, we find 10 that still use an older area code of 567. This is an example of:
dirty data.
inconsistent data.
non-integrated data.
a "wrong format" problem.
a "too much data" problem.
Question 48: A data mart difers from a data warehouse in that:
it has a smaller database.
it deals with a particular component or functional area of the business.
data mart users do not have the data management expertise of data warehouse employees.
Both it has a smaller database and it deals with a particular component or functional area of the business
All of these
Question 49: OLAP stands for:
OnLine Analytical Processing.
OfLine Analytical Processing.
OnLine Analysis Process.
OfLine Analytical Processing.
Lazy, Old And Particular.
Question 50: Data mining techniques are used to find patterns and relationships that can be used to:
report.
classify.
predict.
Both classify and predict
All of these.