Reference no: EM132845961 , Length: 1333 words
Assignment - Lab - Configure IPv6 Addresses on Network Devices
Topology
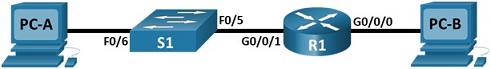
Addressing Table
|
Device
|
Interface
|
IPv6 Address
|
Prefix Length
|
Default Gateway
|
|
R1
|
G0/0/0
|
2001:db8:acad:a::1
|
64
|
N/A
|
|
R1
|
G0/0/1
|
2001:db8:acad:1::1
|
64
|
N/A
|
|
S1
|
VLAN 1
|
2001:db8:acad:1::b
|
64
|
N/A
|
|
PC-A
|
NIC
|
2001:db8:acad:1::3
|
64
|
fe80::1
|
|
PC-B
|
NIC
|
2001:db8:acad:a::3
|
64
|
fe80::1
|
Objectives
Part 1: Set Up Topology and Configure Basic Router and Switch Settings
Part 2: Configure IPv6 Addresses Manually
Part 3: Verify End-to-End Connectivity
Background / Scenario - In this lab, you will configure hosts and device interfaces with IPv6 addresses. You will issue show commands to view IPv6 unicast addresses. You will also verify end-to-end connectivity using ping and traceroute commands.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Note: The default 2960 Switch Database Manager (SDM) template does not support IPv6. It may be necessary to issue the command sdm prefer dual-ipv4-and-ipv6 default to enable IPv6 addressing before applying an IPv6 address to the VLAN 1 SVI.
Required Resources -
- 1 Router (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 2 PCs (Windows with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions -
Part 1: Cable the Network and Configure Basic Router and Switch Settings
After cabling the network, initializing and reloading the router and switch, complete the following:
Step 1: Configure the router
Assign the hostname and configure basic device settings.
Step 2: Configure the switch
Assign the hostname and configure basic device settings.
Part 2: Configure IPv6 Addresses Manually
Step 1: Assign the IPv6 addresses to Ethernet interfaces on R1
a. Assign the IPv6 global unicast addresses, listed in the Addressing Table, to both Ethernet interfaces on R1.
b. Verify that the correct IPv6 unicast address is assigned to each interface.
c. To get the link-local address to match the global unicast address on the interface, manually enter the link-local addresses on each of the Ethernet interfaces on R1.
d. Use a command of your choice to verify that the link-local address has been changed to fe80::1.
e. Which two multicast groups have been assigned to interface G0/0/0?
Step 1: Enable IPv6 routing on R1
a. On a PC-B command prompt, enter the ipconfig command to examine IPv6 address information assigned to the PC interface.
Has an IPv6 unicast address been assigned to the network interface card (NIC) on PC-B?
b. Enable IPv6 routing on R1 using the IPv6 unicast-routing command.
c. Use a command to verify the new multicast group are assigned to interface G0/0/0. Notice that the all-router multicast group (FF02::2) now appears for interface G0/0/0.
d. Now that R1 is part of the all-router multicast group ff02::2, re-issue the ipconfig command on PC-B and examine the IPv6 address information.
Why did PC-B receive the Global Routing Prefix and Subnet ID that you configured on R1?
Step 2: Assign IPv6 addresses to the management interface (SVI) on S1.
a. Assign the IPv6 address for S1. Also assign a link-local address for this interface.
b. Use a command of your choice to verify that the IPv6 addresses are properly assigned to the management interface.
Step 3: Assign static IPv6 addresses to the PCs
a. Open the Ethernet Propertieswindow on for each PC and assign IPv6 addressing.
b. Verify both PCs have the correct IPv6 address information. Each PC should have two Global IPv6 addresses: one static and one SLACC.
Part 2: Verify End-to-End Connectivity
From PC-A,ping fe80::1. This is the link-local address assigned to G0/0/1 on R1.
Ping the S1 management interface from PC-A.
Use the tracertcommand on PC-A to verify that you have end-to-end connectivity to PC-B.
From PC-B, ping the link-local address for G0/0/0 on R1.
Reflection Questions -
1. Why can the same link-local address, fe80::1, be assigned to both Ethernet interfaces on R1?
2. What is the Subnet ID of the IPv6 unicast address 2001:db8:acad::aaaa:1234/64?