Reference no: EM133131818
ASE 4423 Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics - Mississippi State University
Project
Problem Description
Consider a steady, viscous, uniform entrance flow into a two-dimensional plane channel (see Figure 1). The channel walls are separated by a distance 2h in the y-direction. At the entrance (x = 0), the flow is assumed to have a uniform velocity uo directed in the positive x-direction. The flow in the channel is driven by a constant pressure gradient in the streamwise direction (x-direction). Between the inlet plane and the outlet plane (x = xmax), the velocity changes from a uniform profile to a form appropriate for a fully-developed 2D parabolic Poiseuille flow for which ∂u/∂x = 0.
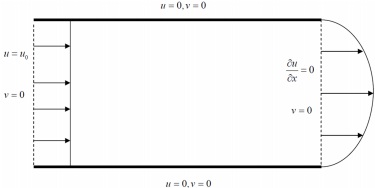
Figure 1: Entrance flow for a 2D plane channel.
Question 1. Using the half-channel height h as a length scale, uo as a velocity scale, and h/uo as a time scale; show that the non-dimensional 2D incompressible Navier-Stokes equations are
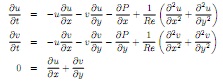
where u = u(x, y) and v = v(x, y) are the non-dimensional velocity components, P (x, y) is the non-dimensional pressure, and Re = uoh/ν is the Reynolds number (ν is the kinematic viscosity).
Question 2. The pressure can be decomposed into a mean pressure P (x) driving the flow and a perturba- tion p(x, y), i.e. P = P (x) + p(x, y). Show that at the outflow the velocity field is
u(y) = 1/2 |C| Re (1 - y2)
where |C| is the constant mean pressure gradient, i.e. ∂P = - |C|. Note that the system of coordinates is chosen such that -1 < y < 1.
Question 3. Use the conservation of mass to show that the constant |C| = 3/Re and that the x-momentum equation can be rewritten as
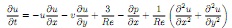
Question 4. Write a numerical code using whichever language you are comfortable with to determine the flow in the channel assuming no-slip, impermeable boundary conditions at the walls: u(x, -1) = u(x, 1) = 0 and v(x, -1) = v(x, 1) = 0; a uniform streamwise velocity at the inflow: u(0, y) = 1 and v(0, y) = 0; and a Neumann boundary condition for the streamwise velocity at the outflow: