Reference no: EM132944269
Section A
Table 1 Crude Oil WTI Apr '20 Options (CLJ20)
Contract size: 1,000 barrels
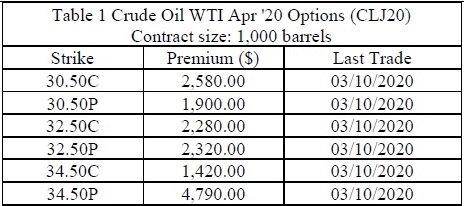
Note: WTI Crude oil was traded at $32.54 on 10th March 2020.
With payoff and profit/loss diagrams, discuss how the following companies would use Crude Oil WTI Apr '20 Options with a strike price of $32.50 for risk management. Calculate the payoff and profit/loss from their option positions if WTI Crude Oil price is $33.50 when the options expire.
Assume WTI Crude Oil and WTI Light Sweet Crude Oil Futures have a perfect positive correlation.
1. On 10th March 2020, an airline company decided to hedge its purchase of 50,000 barrels of WTI Crude Oil in April 2020.
2. On 106 March 2020, an oil producer decided to hedge its sale of 100,000 barrels of WTI Crude Oil in April 2020.
3. Considering the current global situation, should the airline company and the oil producer in Question 1 hedge their positions? If your answer is YES, do you prefer to use crude oil futures or options for the hedging? Explain your reasons.
4. List and explain three trading strategies with option(s) on crude oil that will make you profit from a huge decline in the crude oil price.
A-1 & 2: Discuss the positions and number of contracts to be taken, the maximum profit/loss and the breakeven point.
SECTION B
In this part of your report demonstrates option valuation and interpretation of Greek letters.
1. Calculate the value of a call by applying the binomial pricing model. Explain your calculation.
A stock price is currently £120. Over each period it is expected to go up by 3% or down 2%. The risk- ee interest rate is 2% .er ,eriod. Estimate the value of a European call option on that stock which has a strike price of £120 if the lifetime of the option is: a) one period; and b) two periods.
2. Calculate the value of a put by applying Black-Scholes formula. Carefully explain your calculation.
A stock price is currently £80 and standard deviation is 20%. A European put option on this stock has a strike price of £75 and will expire in 8 months. Continuously compounded risk-free interest rate is 4%. What is the short put value?
3. Explain the "delta" of a call option. (10 marks) Clues for Section B
Bl: start with a binomial tree.
SECTION C
You are given the following information on a series of options on the stock DEF:
Inputs to the Black and Scholes model:
|
Type
|
Put
|
Put
|
Put
|
Call
|
Call
|
Call
|
|
a ¦
|
30%
|
30%
|
30%
|
30%
|
30%
|
30%
|
|
T (yrs) =
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
0.25
|
|
n •
|
2%
|
2%
|
2%
|
2%
|
2%
|
2%
|
|
S •
|
100
|
100
|
100
|
100
|
100
|
100
|
|
X=
|
90
|
100
|
110
|
90
|
100
|
110
|
Outputs from the Black and Scholes model
|
Price
|
1.9051
|
5.7176
|
12.0854
|
12.3540
|
6.2163
|
2.6341
|
|
delta
|
-0.209
|
-0.457
|
-0.701
|
0.791
|
0.543
|
0.299
|
|
gamma
|
0.0191
|
0.0264
|
0.0231
|
0.0191
|
0.0264
|
0.0231
|
|
vega
|
14.3599
|
19.8304
|
17.3603
|
14.3599
|
19.8304
|
17.3603
|
|
theta
|
-8.1603
|
-10.8702
|
-8.7726
|
-9.95132
|
-12.8602
|
-10.9616
|
|
rho
|
-5.6952
|
-12.851
|
-20.5445
|
16.6925
|
12.0243
|
6.8183
|
Inputs to the Black and Scholes model:
1. Using the information above carefully explain how you would form a Long Straddle Strategy on DEF.
2. Determine algebraically the P/L for the above strategy. Use the results to calculate any break-even points for the strategy above.
3. Illustrate the payoff at expiration for the above strategy graphically. Use a range of terminal stock prices from 70 to 130 pence.
4. Obtain and interpret the 'Greeks' for the above strategy.