Reference no: EM133553486
Power Quality and Mitigation
Question:
Nonlinear loads are an essential part of a power system. With the advancement in power electronics, switching elements have a major share in electrical load. These elements create nonlinearities in lines increasing the line losses, reducing power quality and the purity of the sin wave.
In this assessment, you are required to model and analyse the power quality in the Low voltage distribution network due to the impact of non-linear loads and electric vehicle (EV) charging load in a distribution grid. The modelled power system is provided in Figure 1 for reference purpose.
Task 1:
Model the distribution residential network (provided in Fig 1) using DigSilent Power Factory software. This model consists of three phase residential load connected at 0.4 kV voltage level bus bar (which is point of common coupling for analysis) composed of single phase loads. All ratings for powers, harmonic currents [%] and phase angles [°] of measured devices (loads) are given in Table 1.
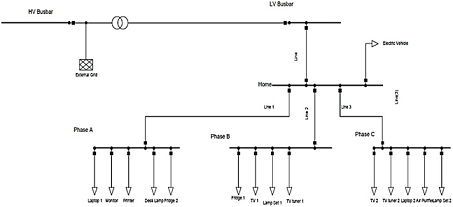
Figure 1: Power Factory Model for reference
Three-phase EV charger is connected in parallel to the residential load. The residential network and loads are connected to distribution network via 1 km overhead line. Consider the impedance of overhead line (0.0414+ j 0.0144) approximately. The rating of HV Busbar is 10 kV and short circuit capacity of 100 MVA. The transformer rating is 16kV, K% =4% and vector group Yyn.
Task 2:
Plot the Current [A] versus Time [s] characteristic of residential load at Phase A, Phase B and Phase C respectively for residential load only. Plot harmonic distortion currents of all three phases at different levels (2nd, 3rd, 5th and so on) and compare highest current distortion levels.
Task 3:
Plot the Voltage [V] versus Time [s] characteristic of residential load at Phase A, Phase B and Phase C respectively for residential load only. Plot harmonic distortion voltages of all three phases at different levels (2nd, 3rd, 5th and so on) and compare highest voltage distortion levels.
Task 4:
In order to assess the influence of EV charging to the harmonic content in the observable residential distribution network, include fragment EV charging current based load model (16 kW) into the previously described model. Present the corresponding result of Current and Voltage harmonic distortion after addition of EV Load. (Refer to tutorial 5 case studies to understand the application of non-linear loads in LV distribution network)
Note: To simulate the charging behaviour of electric vehicles in PowerFactory the template "DIgSILENT Electric Vehicle" from the global library can be used. This is done by using a QDSL (Quasi-Dynamic Simulation Language) model.
Task 5:
Analyse the situation before and after the connection of EV load and explain its impact on the harmonic current and voltage content.