Reference no: EM13768573
1. The aggregate demand curve is negatively sloped in part because of the impact of interest rates on:
A) potential output.
B) net exports.
C) consumption and investment.
D) government purchases.
2. According to the short-run aggregate supply curve, when the _________ rises, the quantity of
_________ rises.
A) profit per unit; aggregate output demanded
B) aggregate price level; aggregate output supplied
C) aggregate price level; aggregate output demanded
D) interest rate; aggregate output supplied
3. The SRAS curve is upward sloping because:
A) a higher aggregate price level leads to lower output as costs of production increase.
B) a higher aggregate price level leads to higher output since most production costs are fixed in the short run.
C) a lower aggregate price level leads to higher output since production costs tend to fall in the short run.
D) a lower aggregate price level leads to higher profit and higher productivity.
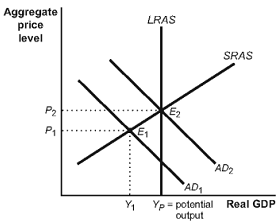
4. Suppose that this economy is in equilibrium at E1. If there is an increase in government purchases, then:
A) AD2 will shift to the left, causing an increase in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
B) AD2 will shift to the left, causing a decrease in the price level and a decrease in the real GDP.
C) AD1 will shift to the right, causing an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
D) AD1 will shift to the right, causing a decrease in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
5. (Figure: Fiscal Policy I) Suppose that this economy is in equilibrium at E2. If there is a decrease in government purchases, then:
A) AD2 will shift to the left, causing an increase in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
B) AD2 will shift to the left, causing a decrease in the price level and a decrease in the real GDP.
C) AD1 will shift to the right, causing an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
D) AD1 will shift to the right, causing a decrease in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
6. (Figure: Fiscal Policy I) Suppose that this economy is in equilibrium at E1. If there is a decrease in taxes, then:
A) AD2 will shift to the left, causing an increase in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
B) AD2 will shift to the left, causing a decrease in the price level and a decrease in the real GDP.
C) AD1 will shift to the right, causing an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
D) AD1 will shift to the right, causing a decrease in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
7. (Figure: Fiscal Policy I) Suppose that this economy is in equilibrium at E2. If there is an increase in taxes, then:
A) AD2 will shift to the left, causing an increase in the price level and a decrease in real GDP.
B) AD2 will shift to the left, causing a decrease in the price level and a decrease in the real GDP.
C) AD1 will shift to the right, causing an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
D) AD1 will shift to the right, causing a decrease in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
8. (Figure: Fiscal Policy I) Suppose that this economy is in equilibrium at E2. If there is an increase in government transfers, then:
A) AD2 will shift to the right, causing an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
B) AD2 will shift to the left, causing a decrease in the price level and a decrease in the real GDP.
C) AD1 will shift to the right, causing an increase in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
D) AD1 will shift to the right, causing a decrease in the price level and an increase in real GDP.
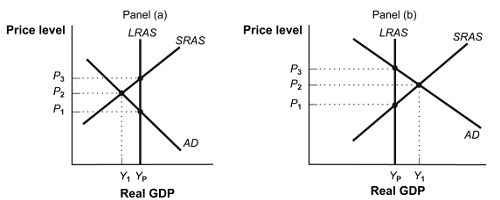
9. (Figure: Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps) In panel (a), an expansionary policy designed to move the economy from Y1 to Yp would attempt to:
A) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by increasing aggregate demand.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right by increasing aggregate demand.
C) shift the SRAS curve to the left.
D) shift the LRAS curve to the left.
10. (Figure: Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps) If the economy is in short-run equilibrium at Y1 in panel (a), the economy is experiencing
A) a recessionary gap
B) an inflationary gap.
C) simultaneous short-run and long-run equilibrium.
D) full employment.
11. (Figure: Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps) If the economy is in short-run equilibrium at Y1 in panel (a), to return to potential output at YP policy makers should
A) use contractionary stabilization policy
B) expansionary stabilization policy.
C) use policies to shift the SRAS to the left.
D) use policies to shift the LRAS to the left.
12. (Figure: Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps) If the economy is in short-run equilibrium at Y1 in panel (b), the economy is experiencing
A) a recessionary gap
B) an inflationary gap.
C) simultaneous short-run and long-run equilibrium.
D) full employment.
13. (Figure: Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps) If the economy is in short-run equilibrium at Y1 in panel (b), to return to potential output at YP policy makers should
A) use contractionary stabilization policy
B) expansionary stabilization policy.
C) use policies to shift the SRAS to the left.
D) use policies to shift the LRAS to the left.
14. (Figure: Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps) If the economy is in short-run equilibrium at Y1 in panel (b), a contractionary policy to bring the economy back to potential output at YP would attempt to
A) shift the SRAS to the left
B) shift the LRAS to the left
C) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by decreasing aggregate demand.
D) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right by increasing aggregate demand.
15. Included in the M1 definition of money are:
A) checkable bank deposits.
B) savings deposits.
C) U.S. Treasury bills.
D) demand deposits, savings deposits, and U.S. Treasury bills.
16. Included in the M2 definition of money is(are):
A) currency in circulation.
B) money market funds.
C) travelers' checks.
D) currency in circulation, money market funds, and travelers' checks.
17. The reserve ratio is the:
A) bank's holdings of gold.
B) government's holdings of gold at Fort Knox.
C) fraction of deposits that banks hold in their vaults plus their deposits at the Federal Reserve.
D) ratio of gold to the paper money in the economy.
18. Bank reserves are:
A) the money in bank vaults only.
B) the amount of cash that a bank must hold to pay FDIC insurance premiums.
C) the currency held at bank vaults plus bank deposits at the Federal Reserve.
D) one hundred percent of checkable bank deposits.
19. The tools of conducting monetary policy include:
A) changes in the required reserve requirement.
B) changes in the prime rate.
C) open market purchases of corporate stock.
D) changing tax rates.
20. To _______ the money supply, the Federal Reserve could ________.
A) increase; decrease the money multiplier
B) decrease; lower the reserve requirements
C) increase; conduct open-market purchases
D) decrease; lower the discount rate
21. Federal funds are:
A) government tax receipts.
B) loans between banks.
C) government expenditures.
D) bank deposits at the Federal Reserve.
22. The discount rate is the interest rate the Federal Reserve charges on loans to:
A) consumers.
B) the federal government.
C) state governments.
D) banks.
23. The three main monetary policy tools are:
A) interest rates, taxes, and government purchases.
B) currency, near-moneys, and reserve ratio.
C) deposit insurance, discount rate, and money multiplier.
D) reserve requirements, the discount rate, and open-market purchases.