Reference no: EM13169298
Dangerously Thin: A Case Study on the Genetic Code
At 65 years old, Henry Blake was in excellent health and enjoying his first year of retirement. Upon returning from his dream trip to the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, he noticed that his left leg was swollen just inferior to the knee. He already had scheduled an appointment for a complete physical, so he knew that in a few days he would be able to have his physician look at his leg.
Dr. Strickland had been the Blake family doctor for more than 40 years. Knowing that Henry had planned to do some traveling, Dr. Strickland opened with a question that Henry initially found to be a bit out of the ordinary.
"Any chance this swelling showed up after a long flight?"
"As a matter of fact it did," Henry replied.
"My gut tells me that you may have a clot in that leg, but we'll have to have a look at it before we'll know for sure."
Dr. Strickland knew that Henry's family had a history of clotting disorders, and he had recently treated Henry's brother for a deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a disorder that gets its name from the blood clots that form in a vein deep within the leg. A DVT was confirmed by the Doppler ultrasonography results (a test that uses sound to create images of blood flow). Dr. Strickland placed Henry on a "blood thinning" drug called warfarin, which works by preventing clots from forming.
Henry returned to his retirement plans but quickly found himself back in Dr. Strickland's office after suffering from frequent nose bleeds. A laboratory test called an INR (International Normalized Ratio) was performed. This test measures the time it takes for blood to clot and compares it to an average. The test revealed that the time it took for Henry's blood to clot was well above what would be expected for the dose of warfarin that he had been placed on. Dr. Strickland immediately took Henry off of his warfarin treatments and asked that he come in every three days for blood tests. Dr. Strickland became concerned when Henry's abnormal INR results continued long after he had stopped taking warfarin.
Through genetic testing, Henry was found to carry a mutation in a gene for an enzyme called CYP2C9. While the strange name of the gene does not really fully appear to capture the importance of its function, it has a role in breaking down more than 15% of the drugs currently in use, and as many as 35% of people carry a slower acting form of this enzyme. The portion of Henry's DNA that codes for the CYP2C9 enzyme contains more than 1,400 nucleotides. Henry carries two copies of the CYP2C9 gene, and the tests showed that both of them contain a mutation. On one of these genes, the 1075th nucleotide has been changed from an adenine (A) to a cytosine (C). This mutation converts an ATT triplet code in the coding strand of the DNA molecule to CTT. In Henry's other CYP2C9 gene, the 430th nucleotide has been changed from a cytosine (C) to a thymine (T). The DNA triplet code CGT in the coding strand becomes TGT as a result of this mutation. Henry was considered a poor metabolizer (PM) because both of his CYP2C9 genes contained a mutation, and therefore he was not making any fully functional enzyme. People who carry two normal copies of the gene are referred to as extensive metabolizers (EM) for their ability to quickly break down drug molecules.
Short Answer Questions
1. Why would someone with this type of mutation be at a much higher risk for overdosing on a prescribed drug?
2. The underlying problem in this case resides in Henry's "genes." From what you know about the function of a gene, explain how this problem led to a malfunction in one of Henry's proteins.
3. The DNA changes that are described in Henry's story are changes to the coding strands of the CYP2C9 genes. What is the function of the coding strand and how does it differ from the function of the template strand of Henry's CYP2C9 gene?
4. Consider the following DNA sequence found on a different portion the coding strand of Henry's CYP2C9 gene: TTACCGAGA
a. What would be the sequence of the template strand on this portion of the gene?
b. How many triplet codes does this DNA sequence contain?
c. What would be the sequence of the mRNA after this sequence is transcribed?
d. How many amino acids does this portion of Henry's coding stand actually code for?
5. In the first mutation of the CYP2C9 gene described in Henry's story, the 1075th nucleotide had changed from an adenine (A) to a cytosine (C). This mutation converts an ATT triplet code in the coding strand of the DNA molecule to CTT. Beginning with this triplet code on the DNA, describe the effect that this change would have on the following:
a. The nucleotide sequence on the template strand of the gene.
b. The mRNA codon that results after this triplet code is transcribed.
c. The anticodon on the tRNA molecule that is complementary to the mRNA codon described above.
d. The amino acid that would be carried by the tRNA molecule described above.
6.In Henry's other CYP2C9 gene, the 430th nucleotide had changed from a cytosine (C) to a thymine (T). This mutation converts a CGT triplet code in the coding strand of the DNA molecule to TGT. Beginning with this triplet code on the DNA, describe the effect that this change would have on the following:
a. The nucleotide sequence on the template strand of the gene.
b. The mRNA codon that results after this triplet code is transcribed.
c. The anticodon on the tRNA molecule that is complementary to the mRNA codon described above.
d. The amino acid that would be carried by the tRNA molecule described above.
7. From what you understand about enzymes, explain why a change in an amino acid would cause Harry's enzyme to lose its function.
8. In both of Henry's mutations, it is the first nucleotide in the DNA triplet code that has been changed.
a. Using the genetic code chart below, create a list of single nucleotide changes in the two affected triplet codes described for Henry's genes that could occur WITHOUT resulting in a change in the amino acid in the enzyme.
NOTE: The code chart below contains mRNA codons and the amino acids associated with those codons. Your list should contain DNA triplet codes.
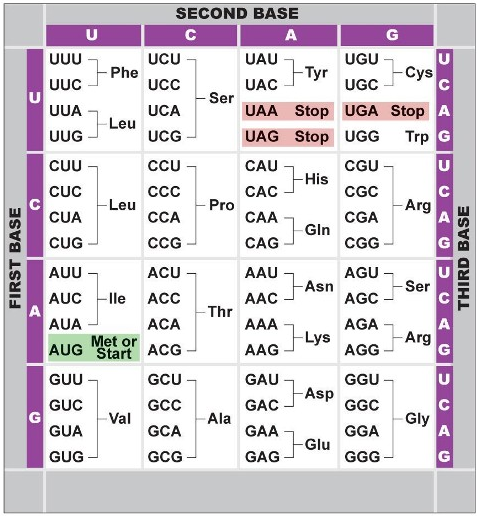
b. How many triplet code changes did you find that could occur WITHOUT resulting in an amino acid change in the enzyme?
c. Which position (first, second, or third) did the changes occur within the DNA triplet codes you listed above?
d. What would you conclude from the pattern that emerged?