According to this theorem, the work done by a force on a particle is same to the change in the kinetic energy of the particle.
We know that the quantity F × dS = F dS cosΘ is described as the work done by force F on the particle during small displacement dS. When the force F performs on the particle during a finite displacement, the work done is calculated as,
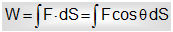 ....(i)
....(i)
Suppose that a object of mass m is performed upon by a resultant acceleration force F along the X-axis. Consider the body moves from a position x1 to position x2 along X-axis. Let the speed of the object increases from v1 and v2. The work done by the force in the displacement is
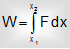 ...(ii)
...(ii)
But according to Newton's second law, 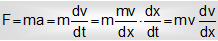
Substituting this value in eq. (2), we get
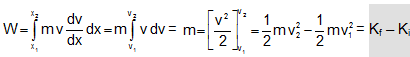 ... (iii)
... (iii)
where the quantity is called 1/2mv2as the kinetic energy of the object. Kf and Ki are the initial and final kinetic energies of the body.
If ΔK be the change in kinetic energies, then
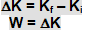
Note: - Work-energy theorem is particularly useful in detemination of minimum stopping force or minimum stopping distance. If a object is brought to a halt, the work done to do so is same to the kinetic energy lost.
Mechanical energy:
Mechanical energy E of particle, system or object is described as the sum of kinetic energy K and potential energy U, i.e. E = K + U. It is a scalar quantity having dimensions [ML2T-2] and SI unit joule.
(i) It relays on frame of reference.
(ii) A body may have mechanical energy without having either kinetic energy or potential energy. However, if both potential and kinetic energies are zero, mechanical energy will be zero. The result may or may not be true, i.e., if E = 0 either both KE and PE are zero or PE negative and KE positive such that KE + PE = 0.
Examples: Law of conservation of mechanical power
|
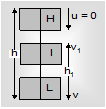
(a) Freely falling body: At the highest point, net energy is in the form of potential power. At an intermediate point, energy is in the form of both KE and PE. At the lowest point, net energy is in the form of only KE.
TE = (PE)H = (KE)I + (PE)I = (KE)L 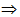
|
|
|
(b) Body projected vertically upwards: At the initial point total energy is in the form of KE only, at an intermediate point energy is in the form of both KE and PE and at the highest point total energy is in the form of only PE.
TE = (KE)L = (KE)l + (PE)l = (PE)H 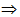
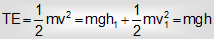
|
|
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Work Energy Theorem questions? Work Energy Theorem topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Work Energy Theorem related problems. We provide step by step Work Energy Theorem question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Work Energy Theorem topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours