Volumetric analysis
Volumetric analysis is a quantitative analysis. It involves the measurement of the volume of a known solution required to bring about the completion of the reaction with a measured volume of the unknown solution.
Titration : The process of addition of the known solution from the burette to the measured volume of solution of the substance to be estimated until the reaction between the two is just done, is known as titration. Thus, a titration involves two solutions;
(i) Unknown solution : The solution consisting the substance to be estimated is termed unknown solution. The substance is termed titrate.
(ii) Standard solution : The solution in which an accurately known amount of the reagent (titrant) has been dissolved in a known volume of the solution is termed standard solution. There are two types of reagents (titrants) :
(a) Primary standards : These can be accurately weighed and their solutions are not to be standardised before use. Oxalic acid (H2C2O4.2H2O), potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7), silver nitrate (AgNO3), copper sulphate (CuSO4.5H2O), ferrous ammonium sulphate [FeSO4(NH4)2SO2.6H2O], sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3.5H2O), etc., are the examples of primary standards.
(b) Secondary standards : The solutions of these reagents are to be standardised before use as these cannot be weighed accurately. The examples are potassium hydroxide (KOH), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), hydrochloric acid (HCl), potassium permanganate (KMnO4), iodine, sulphuric acid (H2SO4)etc.
Law of equivalence : It is applied in all volumetric estimations. According to it, the chemical substances react in the ratio of their chemical equivalent masses.
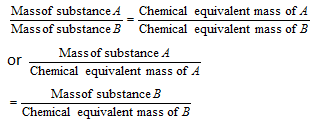
or gram equivalent of A = gram equivalent of B
or milli-gram equivalent of A = milli-gram equivalent of B
The point at which the amounts of the two reactants are just equivalent is known as equivalence point or end point. An auxiliary substance which helps in the usual detection of the completion of the titration or equivalence point or end point is termed as indicator, i.e., substances which undergo some easily detectable changes at the equivalence point are used as indicators.
Methods of showing concentrations of solutions
The concentration of a solution can be given in several ways.
(1) Percent by mass
(2) Molarity
(3) molality
(4) Mole fraction
(5) Normality
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Volumetric Analysis-Titrations questions? Volumetric Analysis-Titrations topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Volumetric Analysis-Titrations related problems. We provide step by step Volumetric Analysis-Titrations question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Volumetric Analysis-Titrations topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours