The variation of electronegativity in the periodic table
(i) In the period, electronegativity increases from left to right. This is because of decrease in size and increase in nuclear charge. Therefore the alkali metals have the lowest value, while the halogens have the highest. The inert gases posses zero electronegativity.
(ii) In a group, electronegativity decreases from top to bottom. This is because of increase in atomic size.
If an element exhibits various oxidation state, the atom in higher oxidation state will be more negative because of greater attraction for the electron, for example Sn II (1.30) and Sn IV (1.90).
(3) Electronegativity can be expressed on the following three scales
(i) Mulliken's scale : Mulliken regarded electronegativity as the average value of ionization potential and electron affinity of an atom.
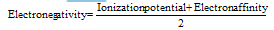
(ii) Allred-Rochow scale : Allred and Rochow defined electronegativity as the electrostatic force exerted by the nucleus on the valence electrons. Thus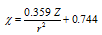 where Z is the effective nuclear charge and r is the covalent radius of the atom in Å.
where Z is the effective nuclear charge and r is the covalent radius of the atom in Å.
(iii) Pauling scale : Pauling scale of electronegativity is the most widely used. This is based on the excess of bond energies. He described electronegativity difference between the two atoms and then by assigning arbitrary values to few elements (for example 4.00 to fluorine, 2.5 to carbon and 2.1 to hydrogen), he then calculated electronegativity of the other elements.
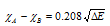
where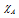 and
and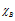 are electronegativities of the atoms A and B respectively, the factor 0.208 comes from the conversion of kcal to electron volt (1 eV = 23.0 kcal/mole),
are electronegativities of the atoms A and B respectively, the factor 0.208 comes from the conversion of kcal to electron volt (1 eV = 23.0 kcal/mole),
while ΔE = Actual bond energy 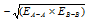
Pauling and Mulliken values of electronegativities are related as below 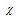 (Pauling) = 0.34
(Pauling) = 0.34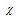 (Mulliken) - 0.2
(Mulliken) - 0.2
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Variation of electronegativity in the periodic table questions? Variation of electronegativity in the periodic table topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Variation of electronegativity in the periodic table related problems. We provide step by step Variation of electronegativity in the periodic table question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Variation of electronegativity in the periodic table topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours