UNIX/LINUX Directory Structure can be understood as follows
Dennis Ritchie and Ken Thomsom wrote the UNIX language at the Bell Labs in the year 1969. It was initially written in the assembly language and a high- level language called Bit was later converted from B language to C language. Linus Torvalds, an undergraduate student at University of Helsinki, Finland, wrote the Linux in 1991. It is amongst one of the most popular operating systems, certainly for the PCs.
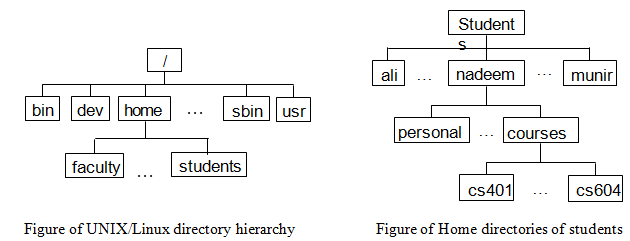
UNIX has a hierarchical file system structure comprising of a root directory (denoted as /) with the other directories and files hanging under it. UNIX uses a directory hierarchy which is commonly represented as the folders. However, in its place of using graphical folders typed commands (in the command line user interface) are used to navigate system. Particular files are then represented by paths and filenames similarly as they are in html addresses. A pathname is the list of directories which is separated by the slashes (/). If a pathname starts with a /, it refers to root directory. The last component of a path might be a file or the directory. A pathname might simply be a file or the directory name. For instance, /usr/include/sys/param.h, ~/courses/cs604, and prog1.c are the pathnames.
When you log in, system places you in the directory known as your home directory (also known as login directory). You may refer to your home directory by using ~ or $PATH in Bash, Bourne shell, and the Korn shells and by using $path in C and TC shells. Shells also understand relative and absolute pathnames both. An absolute pathname begins with the root directory (/) and a relative pathname begins with your home directory, your current directory, or parent of your current directory (the directory which you are currently in). For instance, /usr/include/sys/param.h is the absolute pathname and ~/courses/cs604 and prog1.c are the relative pathnames.
You can refer to your present directory by using . (pronounced dot) and parent of your current directory by using .. (pronounced dotdot). For instance, if nadeem is currently in courses directory, he can refer to his home directory by using the .. and his personal directory by making use of ../personal. Likewise, he can refer to directory for this course by using cs604.
Figures drawn below shows sample directory structures in a UNIX/Linux system. The user nadeem has a subdirectory under his home directory, known as courses. This directory comprises subdirectories for the courses which you have taken, including one for this course as well.
Email based Operating System assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching Operating System expert for help with Unix/Linux Directory Structure questions? Unix/Linux Directory Structure topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of operating system assignment help and operating system homework help. Live experts are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Unix/Linux Directory Structure related problems. We provide step by step Unix/Linux Directory Structure question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Unix/Linux Directory Structure topic under operating system theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced tutors network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving operating system questions in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours