Types of rocket propellants:
Depending upon the physical state, propellants can be classified as:
(i) Solid propellants: The solid propellants are mixtures of solid fuel and a solid oxidizer. These are further divided into two classes,
(a) Composite propellants: These are solid propellants which use polymeric binder such as polyurethane or polybutadiene as a fuel and a solid oxidizer such as ammonium perchlorate, chlorate or nitrate. The performance of these propellants can be increased by using some additives such as finely divided magnesium or aluminum metal along with the fuel.
(b) Double base propellants: These are solid propellants which mainly use nitroglycerine and nitrocellulose. The nitrocellulose sets in nitroglycerine set in as a solid mass.
The main disadvantage of solid propellants is that these propellants once ignited will continue burning with pre calculated rate. These may not be regulated.
(ii) Liquid propellants: These consist of an oxidizer such as liquid oxygen, nitrogen tetroxide (N2O2) or nitric acid and a fuel such as alcohol, hydrazine, liquid hydrogen and kerosene. These are further divided as,
(a) Monopropellants: The propellants in which a single chemical compound acts as fuel as well as oxidizer are called monopropellants. As, nitro methane, methyl nitrate, hydrogen peroxide, hydrazine, etc. Except hydrazine, the other compounds contain both the oxidizer and the fuel elements in the same molecule.
(b) Bipropellants: These are propellants in which the fuel and oxidizer are stored separately but are allowed to combine at the time of combustion. For example, liquid oxygen and kerosene.
- Hydrazine can react both as a monoliquid as well as a biliquid propellant. Hydrazine (H2N-NH2) acts as a monoliquid propellant as it decomposes exothermally into hot gaseous mixture of N2 and H2,
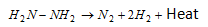
As a biliquid propellant with liquid oxygen as oxidizer,
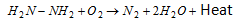
Advantages of Biliquid Propellants over Solid Propellants
- The biliquid propellants produce higher thrust than solid propellants.
- The thrust generated by liquid propellants can be controlled by switching on and off the flow of propellants. On the other case, the thrust may not be controlled in solid propellants.
(iii) Hybrid propellants: These are the propellants which consist of solid fuel and a liquid oxidiser. For example, liquid N2O4 (liquid oxidizer) and acrylic rubber (solid fuel).
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Types of rocket propellants questions? Types of rocket propellants topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Types of rocket propellants related problems. We provide step by step Types of rocket propellants question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Types of rocket propellants topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours