Theory of the radioactivity disintegration can be understood as follows
Rutherford and Soddy, in the year1903, postulated that the radioactivity is a nuclear phenomenon and all the radioactive changes are taking place in nucleus of the atom. They presented the interpretation of the radioactive processes and the origin of the radiations in the form of a theory termed as theory of radioactive disintegration. The major points of this theory are given below,
(1) The atomic nuclei of radioactive elements are unstable and liable to disintegrate at any moment.
(2) The disintegration is spontaneous process that is constantly breaking. The rate at which the breaking takes place is not affected by the external factors such as pressure, temperature, chemical combination etc.
(3) During the process of the disintegration, atoms of the new elements called daughter elements possessing different physical and chemical properties than the parent elements come into existence.
(4) During the process of disintegration, either alpha or beta particles are emitted from nucleus of the atom.
The disintegration process can proceed in one of the below stated two ways,
(i) α -particle emission : When an α-particle (2He4) is emitted from the nucleus of an atom of the parent element, the nucleus of the new element, called daughter element possesses atomic mass or atomic mass number less by four units and nuclear charge or atomic number less by 2 units because α -particle has mass of 4 units and nuclear charge of two units.
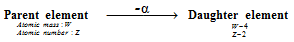
(ii) β-particle emission : β -particle is merely an electron which has negligible mass. Whenever the beta particle is emitted from nucleus of a radioactive atom, nucleus of the new element formed possesses the similar atomic mass but nuclear charge or the atomic number is increased by 1 unit than parent element. Beta particle emission is because of the result of decay of neutron into proton and electron.
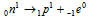
The electron which is produced escapes as a beta-particle-leaving proton in the nucleus.
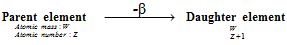
(iii) γ-ray emission: γ -rays are emitted due to the secondary effects. The excess of the energy is released in the form of γ -rays. Thus γ -rays arise from energy re-arrangements in the nucleus. As γ -rays are short wavelength electromagnetic radiations with no mass and no charge, their emission from the radioactive element does not produce any new element.
Special case : If in the radioactive transformation 1 alpha and 2 beta-particles are emitted, then the resulting nucleus possesses the same atomic number but atomic mass is less by four units. The radioactive transformation of this type always produces an isotope of the parent element.
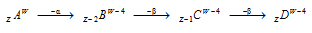
A and D are isotopes.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Theory of the radioactivity disintegration questions? Theory of the radioactivity disintegration topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Theory of the radioactivity disintegration related problems. We provide step by step Theory of the radioactivity disintegration question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Theory of the radioactivity disintegration topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours