Set theoretic principles:
If 'A' and 'B' be any 2 events of sample space then
- A∪B would stand for the occurrence of at least 1 of them.
- A∩B stands for the simultaneous occurrence of A and B.
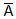 (or A') stands for the non occurrence of A
(or A') stands for the non occurrence of A 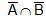 (or A' ∩ B') stands for non occurrence of A and B both.
(or A' ∩ B') stands for non occurrence of A and B both.- A ⊆ B stands for 'occurrence of A implies occurrence of B'.
- If A and B are any 2 events, then P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A∩B)
- If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B).
In this case there will not be any sample point present in A∩B.
As, A∪A' = S and A and A' are mutually exclusive events
=> P(A∪A') = P(A) + P(A') = P(S) = 1 => P(A') = 1 - P(A).
- P(A ∩ B') = P(A) - P(A ∩ B)
As A∩B' and A∩B are mutually exclusive events and (A∩B')∪(A∩B) = A
=> P(A∩B') + P(A∩B) = P(A) => P(A∩B') = P(A) - P(A∩B)
Likewise, P(A'∩B) = P(B) - P(A∩B)
As, (A'∪B') ∪ (A∩B) = S
=> P(A'∪B') + P(A ∩ B) = 1 => P(A' ∪ B') = 1 - P(A∩B)
Likewise, P(A' ∩ B') = 1 - P(A∪B)
- P(exactly one of A, B occurs)
= P(A∩B') + P(A'∩B) = P(A) + P(B) - 2P(A∩B)
= P(A∪B) - P(A∩B) = P(A' ∪ B') - P(A' ∩ B')
If A, B, C are any 3 events of sample space, then
- P(A∪B∪C) = P(A) + P(B) + P(C) - P(A ∩ B) - P(A ∩ C) - P(B ∩ C) + P(A ∩ B ∩ C)
- P (Exactly 1 of A, B, C occurs)
= P(A) + P(B) + P(C) - 2P(A∩B) - 2A(A∩C) - 2P(B∩C) + 3P(A∩B∩C)
- P(Exactly 2 of A, B, C occur) = P(A ∩ B) + P(B ∩ C) + P(A ∩ C) - 3P(A ∩ B ∩ C)
- P (at least 2 of A, B, C occur) = P(A ∩ B) + P(B ∩ C) + P(A ∩ C) - 2P(A ∩ B ∩ C)
- If A1, A2 L , An are ¢n' events, then P(A1∪ A2 L ∪An)
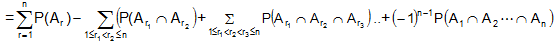
- P (A ∪ B) ≥ max (P(A), P(B), P(A) + P(B) - 1)
as A ⊆ A∪ B => P(A) ≤ P(A∪B)
Like wise, B ⊆ A ∪ B => P(B) ≤ P(A∪B) => P(A∪B) ≥ Max (P(A), P(B))
Also P(A∪B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A ∩ B)
P(A) + P(B) - 1 ≤ P(A∪B) ≤ P(A) + P(B) (As 0 ≤ P(A ∩ B) ≤ 1)
Max (P(A) + P(B) - 1, P(A), P(B)) ≤ P(A∪B) ≤ P(A) + P(B)
- If out of m + n likely, mutually exclusive and exhaustive cases, m cases are favorable to the A event and n are not favorable to the event A, m : n is called as odds in favour of A, n : m is called as odds against the event A.
Email based Set theoretic principles Assignment Help -Set theoretic principles Homework Help
We at www.expertsmind.com offer email based Set theoretic principles assignment help - homework help and projects assistance from k-12 school level to university and college level and engineering and management studies. We provide finest service of Mathematics assignment help and Mathematic homework help. Our experts are helping students in their studies and they offer instantaneous tutoring assistance giving their best practiced knowledge and spreading their world class education services through e-Learning program.
Expertsmind's best education services
- Quality assignment-homework help assistance 24x7 hrs
- Best qualified tutor's network
- Time on delivery
- Quality assurance before delivery
- 100% originality and fresh work