Rules for the determination of oxidation number of an atom : The following rules are followed in ascertaining the oxidation number of an atom,
(i) If there is a covalent bond between two same atoms then oxidation numbers of these two atoms will be zero. The bonded electrons are symmetrically distributed between two atoms. The Bonded atoms do not acquire any charge. So the oxidation numbers of these two atoms are zero.
A : A or A - A A* + A*
For instance, Oxidation number of Cl in Cl2, O in O2 and N in N2 is zero.
(ii) If covalent bond is between two different atoms then electrons are counted towards more electronegative atom. Therefore oxidation number of more electronegative atom is negative and oxidation number of less electronegative atom is positive. The total number of charges on any element depends on the number of bonds.
A - B A+ + B- :
A - B A+2 + : B-2 :
Oxidation number of the small electronegative element (A) is + 1 and + 2 respectively.
(iii) If there is the coordinate bond between the two atoms then oxidation number of donor atom will be + 2 and of acceptor atom will be - 2.
A B A2+ + :B-2 :
(iv) The oxidation number of all the atoms of different elements in their respective elementary states is taken to be zero. For example, in N2, Cl2, H2, P4, S8, O2, Br2, Na, Fe, Ag etc. the oxidation number of each atom is zero.
(v) The oxidation number of a monoatomic ion is the same as the charge on it. For instance, oxidation numbers of Na+, Mg2+ and Al3+ions are + 1, + 2 and + 3 respectively while those of Cl-, S2- and N3- ions are -1, -2 and -3 respectively.
(vi) The oxidation number of hydrogen is + 1 when combined with non-metals and is -1 when combined with active metals called metal hydrides such as LiH, KH, MgH2, CaH2 etc.
(vii) The oxidation number of oxygen is - 2 in most of its compounds, except in peroxides like H2O2, BaO2 etc. where it is -1. Another interesting exception is found in the compound OF2 (oxygen difluoride) where the oxidation number of oxygen is + 2. This is due to the fact that fluorine being the most electronegative element known has always an oxidation number of -1.
(viii) In the compounds formed by the union of metals with non-metals, the metal atoms will have positive oxidation numbers and the non-metals will have negative oxidation numbers.
For example,
(a) The oxidation number of alkali metals (Li, K Na, etc.) is always +1 and those of alkaline earth metals (Be, Mg, Ca etc) is + 2.
(b) The oxidation number of the halogens (Cl, F, Br, I) is always -1 in metal halides such as KF, AlCl3, MgBr2, CdI2 etc.
(ix) In the compounds formed by the union of different the elements, the more electronegative atom will have negative oxidation number whereas the less electronegative atom will have positive oxidation number.
The examples are as follows,
(a) N is given the oxidation number of -3 when it is bonded to less electronegative atom as in NH3 and NI3, but is given an oxidation number of + 3 when it is bonded to more electronegative atoms as in NCl3.
(b) Since the fluorine is the most electronegative element known so its oxidation number is always -1 in its compounds that is oxides, interhalogen compounds etc.
(c) In interhalogen compounds of Br, Cl, and I; the more electronegative of the two halogens gets the oxidation number of -1. For example, in BrCl3, the oxidation number of Cl is -1 while that of Br is +3.
(x) For neutral molecule, the sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms is equal to zero. For instance, in NH3 the sum of the oxidation numbers of nitrogen atom and 3 hydrogen atoms is equal to zero. For the complex ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms is equal to charge on the ion. For instance, in SO42- ion, the sum of the oxidation numbers of sulphur atom and 4 oxygen atoms must be equal to -2.
(xi) It may be noted that oxidation number is also frequently called as oxidation state. For instance, in H2O, the oxidation state of hydrogen is +1 and the oxidation state of oxygen is - 2. This means that the oxidation number gives oxidation state of an element in a compound.
(xii) In the case of representative elements, highest oxidation number of the element is the same as its group number while highest negative oxidation number is equal to (8 - Group number) with negative sign with a few exceptions. The most usual oxidation states of the representative elements are shown in the following table,
|
Group
|
Outer shell configuration
|
Common oxidation numbers (states)
except zero in free state
|
|
I A
|
ns1
|
+1
|
|
II A
|
ns2
|
+2
|
|
III A
|
ns2np1
|
+3, +1
|
|
IV A
|
ns2np2
|
+4,+3,+2,+1, -1, -2, -3, -4
|
|
V A
|
ns2np3
|
+5,+3,+1, -1, -3
|
|
VI A
|
ns2np4
|
+6,+4,+2,-2
|
|
VII A
|
ns2np5
|
+7,+5,+3, +1, -1
|
(xiii) The transition metals exhibit the large number of oxidation states due to involvement of (n -1) d electron besides ns electron.
(xiv) The oxidation number of the metal in carbonyl complex is always zero.
Example : Ni has zero oxidation state in [Ni(CO)4].
(xv) Those compounds which posses only C, H and O the oxidation number of carbon can be calculated by following formula,
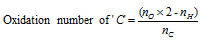
Where, no is the number of oxygen atom, nH is the number of hydrogen atom, nc is the number of carbon atom.
For example, (a) 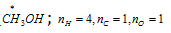 ;
;
Oxidation number of 'C' = 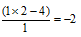
(b) 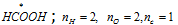 ;
;
Oxidation number of carbon = (2*2-2)/1 = +2
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Rules for determination of oxidation number questions? Rules for determination of oxidation number topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Rules for determination of oxidation number related problems. We provide step by step Rules for determination of oxidation number question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Rules for determination of oxidation number topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours