Law of radioactive disintegration: According to Rutherford and Soddy law for radioactive decay is as follows, "At any point the rate of decay of radioactive atoms is proportional to the number of atoms present at that instant"
i.e. -dN/dt ∝ N =>dN/dt = -λn . It can be proved that N = N0e-λt
This equation can also be written in terms of mass i.e. M = M0e-λt
where N = Number of atoms remains undecayed after time t, N0 = Number of atoms present initially
(i.e. at t = 0), M = Mass of radioactive nuclei at time t, M0 = Mass of radioactive nuclei at time t = 0,
N0 - N = Number of disintegrated nucleus in time t
dN/dt= rate of decay, λ = Decay constant or disintegration constant or radioactivity constant or Rutherford Soddy's constant or the probability of decay per unit time of a nucleus.
Activity: It is defined as the rate of disintegration (or count rate) of the substance (or the number of atoms of any material decaying per second) i.e. A=-dN/dt = λN = λN0e-λt = A0e-λt
where A0 = Activity of t = 0, A = Activity after time t
Units of activity (Radioactivity): It's units are Becqueral (Bq), Curie (Ci) and Rutherford (Rd)
1 Becquerel = 1 disintegration/sec
1 Rutherford = 106 dis/sec,
1 Curie = 3.7 ´ 1011 dis/sec
Half life (T1/2): Time interval in which the mass of a radioactive substance or the number of it's atom reduces to half of it's initial value is called the half life of the substance.
|
i.e. if  then then
Hence from
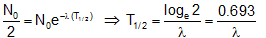
|
|
|
Successive Disintegration and Radioactive Equilibrium: Suppose a radioactive element A disintegrates to form another radioactive element B which intern disintegrates to still another element C; such decays are called successive disintegration.
|
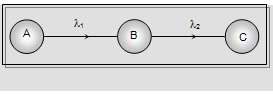
|
Rate of disintegration of 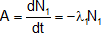 (which is also the rate of formation of B)
(which is also the rate of formation of B)
Rate of disintegration of 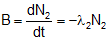 Net rate of formation of B = Rate of disintegration of A - Rate of disintegration of B = λ1N1 - λ2N2
Net rate of formation of B = Rate of disintegration of A - Rate of disintegration of B = λ1N1 - λ2N2
Equilibrium: In radioactive equilibrium, the rate of decay of any radioactive product is just equal to it's rate of production from the previous member.
i.e. 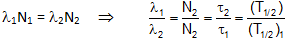
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Radioactive disintegration questions? Radioactive disintegration topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Radioactive disintegration related problems. We provide step by step Radioactive disintegration question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Radioactive disintegration topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours