|
Group
|
Basic radicals
|
Group reagent
|
Ppt. as
|
Explanation
|
|
I
|
Ag+, Hg22+(I), Pb2+
|
dil HCl
|
Chloride
(AgCl, Hg2Cl2, PbCl2)
|
Ksp values of chlorides are low, hence precipitated. Others have higher values hence not precipitated.
|
|
II
|
Cu2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Hg2+(II), Bi3+, As3+, Sb3+, Sn2+
|
H2S gas in presence of dil. HCl
|
Sulphides (CuS, As2S3 etc.)
|
Ksp values of sulphides are low hence precipitated by low [S2-] ion. HCl (with common H+ ion) decreases ionization of H2S which gives low [S2-]. Hence II group is precipitated. Others with higher Ksp values not precipitated.
|
|
III
|
Al3+, Cr3+, Fe3+
|
NH4OH in presence of NH4Cl
|
Hydroxide, Al(OH)3 etc.
|
Ksp values of Al(OH)3 etc. are low. NH4Cl (with common NH4+ ion) decreases ionization of NH4OH giving low [OH-]. Hence group III is precipitated.
|
|
IV
|
Zn2+, Ni2+, Mn2+, Co2+
|
H2S in ammonical medium
|
Sulphides (ZnS etc.)
|
Ksp values of sulphides of group IV are high hence precipitation takes place in higher [S2-]. Basic medium increases ionization of H2S increasing [S2-] hence precipitation of group IV.
|
|
V
|
Ca2+, Ba2+, Sr2+
|
(NH4)2CO3 + NH4Cl
|
Carbonates (CaCO3 etc.)
|
Ksp values of carbonate are less than that of group VI (Mg2+) hence precipitation before Mg2+.
|
|
VI
|
Mg2+, (Na+, K+ also included)
|
NH4OH + Na2HPO4 (only for Mg2+)
|
White ppt. (MgHPO4)
|
-
|
|
0 (Zero)
|
NH4+
|
-
|
-
|
Tested independently from original solution.
|
Chemical reactions added in the tests of basic radicals
Group I : When dil. HCl is added to real solution, silver mercurous mercury, insoluble chlorides of lead are precipitated.
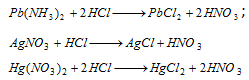
Pb2+ (lead)
(i) PbCl2 is soluble in hot water and on cooling white crystals are again formed.
(ii) The solution of pbcl2 gives a yellow precipitate with potassium chromate solution which is insoluble in acetic acid but soluble in sodium hydroxide.
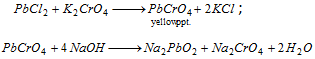
(iii) The solution of PbCl2 forms a yellow precipitate with potassium iodide solution.
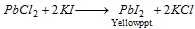
(iv) White precipitate of lead sulphate is formed with dilute H2SO4 The precipitate is soluble in ammonium acetate solution,
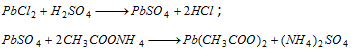
Ag+(silver)
(i) AgCl dissolves in ammonium hydroxide, 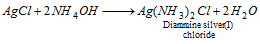
(ii) On adding dilute HNO3 to the above reaction, white precipitate is again generated
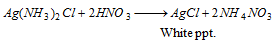
(iii) On including KI to the complex solution, yellow precipitate is obtained.
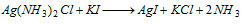
Hg22+ (mercurous)
(i) Hg2Cl2 turns black with NH4OH, 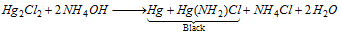
(ii) The black residue mix in aqua-regia forming mercuric chloride.
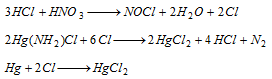
(iii) The solution of HgCl2 forms white or slate-coloured precipitate with stannous chloride.
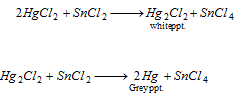
(iv) The solution of HgCl2 with copper turning forms a grey deposit.
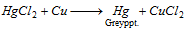
Group II : When hydrogen sulphide is passed in acidified solution, the radicals of second group are precipitated as sulphides. The precipitate is acted with yellow ammonium sulphide. The sulphides of IIB are first oxidised to higher sulphides which then dissolve to form thio-compounds.
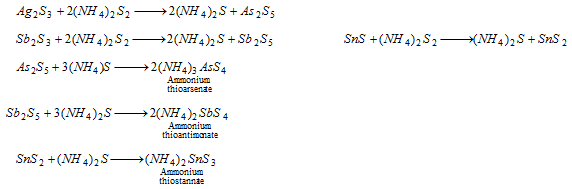
All the three are soluble.
In case, the precipitate does not solvent in yellow ammonium sulphide, it may be either HgS or PbS or Bi2S3 or CuS or CdS The precipitate is heated with dilute HNO3 Except HgS, all other sulphides of IIA are soluble.
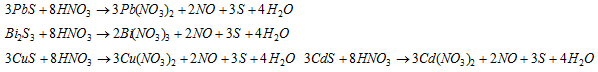
Hg2+ (mercuric)
HgS is dissolved in aqua-regia,
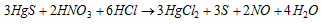
The solution is split into two reactions:
Part I : Stannous chloride solution reduces HgCl2 first into white Hg2Cl2 and then to grey metallic mercury.
Part II : Copper displaces Hg from HgCl2 which gets coated on copper turnings as a shining deposit.
Pb2+ (lead)
In case the sulphide dissolves in dilute HNO3 a small part of the solution is taken. Dilute H2S04 is added. If lead is acted, a white precipitate of lead sulphate seems as, 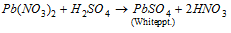
In absence of lead, the remaining solution is made alkaline by the addition of excess of NH4OH. Bismuth forms a white precipitat of Bi(OH)3 copper forms a deep blue coloured solution while cadmium forms a colourless soluble complex,

Bi3+ (bismuth) : The precipitate dissolves in dilute HCl, 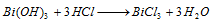
Part I : Addition of excess of water to BiCl3 solution gives a white precipitate due to hydrolysis.
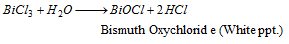
Part II : The solution of BiCl3 is treated with sodium stannite when a black precipitate of metallic bismuth is formed,
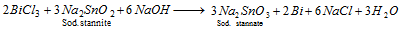
Cu2+ (copper) : Blue coloured solution is acidified with acetic acid. When potassium ferrocyanide is reacted a chocolate coloured precipitate is formed,
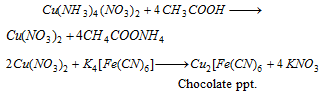
Cd2+ (cadmium) : H2S is passed through colourless solution. The appearance of yellow precipitate confirms the presence of cadmium,
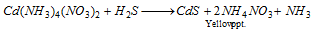
Group IIB : In case the precipitate dissolves in yellow ammonium sulphide, the tests of the radicals arsenic, antimony and tin are performed. The sulphide is reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Antimony and tin sulphide dissolve while arsenic sulphide remains insoluble.
As3+ (arsenic) : The insoluble sulphide is treated with concentrated nitric acid which is then heated with ammonium molybdate. Yellow precipitate of ammonium arsenomolybdate is formed.
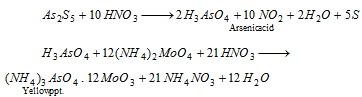
Sn2+ or Sn4+ (tin) : Solution of sulphide in concentrated HCl is reduced with iron fillings or granulated zinc.
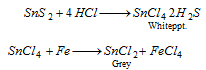
HgCl2 solution is added to above solution which provides first a white precipitate that turns to grey.
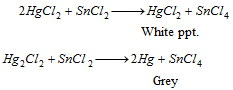
Sb2+ (antimony) : Filtrate of sulphide in concentrated HCl is divided into two parts.
Part I : On dilution with heavy of water, a white precipitate of antimony oxychloride is obtained.
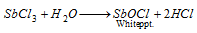
Part II : H2S is circulated. Orange precipitate is formed, 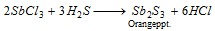
Group III : Hydroxides are precipitated on addition of excess of ammonium hydroxide in presence of ammonium chloride.
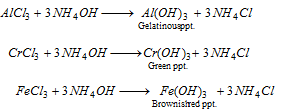
Fe3+ (iron) : The brownish red precipitate dissolves in dilute HCl. The solution is divided into two parts.
Part I : K4[Fe(CN)6] solution is added which forms deep blue solution or precipitate.
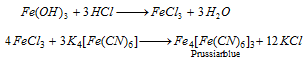
Part II : indication of potassium thiocyanate solution gives a blood red colouration.
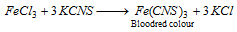
Cr3+(chromium) : The green precipitate is reacted with fusion mixture(Na2CO3 + KNO3) The fused product is extracted with water or the precipitate is heated with NaOH and bromine water.
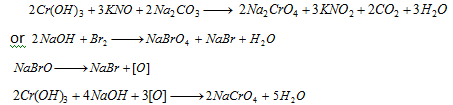
The solution thus obtained contains sodium chromate. The reaction is acidified with acetic acid and treated with lead acetate solvent. A yellow precipitate forms.
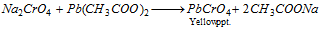
Al3+(aluminium) : The gelatinous precipitate dissolves in NaOH, 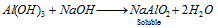
The solution is heated with ammonium chloride when Al(OH)3 is again formed.

Group IV : On passing H2S through the filtrate of the third group, sulphides of fourth group are precipitated. CoS and NiS are black and insoluble in concentrated HCl while MnS (buff coloured), ZnS (colourless) are resolve in conc. HCl.
Zn2+ (zinc) : The sulphide dissolves in HCl. 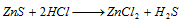
When the solution is treated with NaOH first a white precipitate appears which dissolves in excess of NaOH
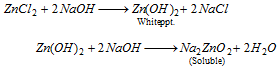
On passing H2S, white precipitate of zinc sulphide is formed 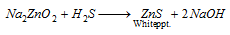
Mn2+ (manganese) : Manganese sulphide dissolves in HCl
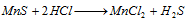
On heating the solution with NaOH and Br2-water, manganese dissolve gets precipitated.
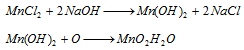
The precipitate is treated with excess of nitric acid and PbO2 or Pb3O4 (red lead). The contents are heated. The formation of permanganic acid imparts pink colour to the supernatant liquid.
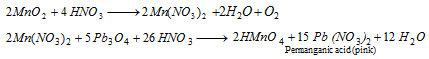
The above test fails in reaction of HCl.
Ni2+ (nickel) and Co2+ (cobalt)
The black precipitate is dissolved in aqua- regia.
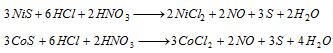
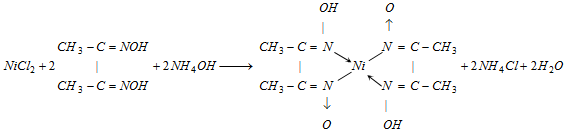
The solution is evaporated to dryness and residue extracted with dilute HCl. It is divided into three parts.
Part I : Add NH4OH (excess) and dimethyl glyoxime. A rosy red precipitate seems, if nickel is present,
Part II : Add CH3COOH in excess and KNO2 The appearance of yellow precipite confirms the presence of cobalt.
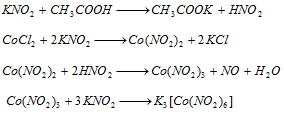
Part III : Solution containing either nickel or cobalt is treated with NaHCO3 and bromine water. Appearance of apple green colour is appeared, the solution is heated when black precipited is formed, which shows the presence of nickel, 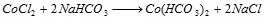
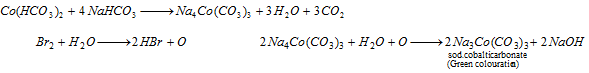
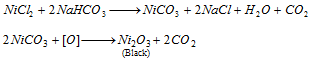
Group V : Ammonium carbonate precipitates V group radicals in the form of carbonates are soluble in acetic acid.
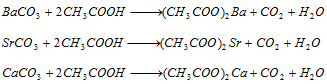
Ba2+ (barium) : Barium chromate is insoluble and precipitated by the addition of potassium chromate solution, 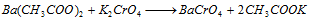
Sr2+ (Strontium) : Strontium sulphate is insoluble and precipitated by the addition of ammonium sulphate solution, 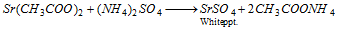
Ca2+ (calcium) : Calcium oxalate is insoluble and precipitated by the addition of ammonium oxalate.
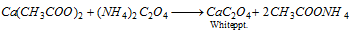
Group VI : In the filtrate of V group, some value of ammonium oxalate is included as to remove Ba, Ca and Sr completely from the solution. The clear solution is concentrated and prepared alkaline with NH4OH Disodium hydrogen phosphate is now included, a white precipitate is created.
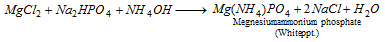
Zero group NH4+ (ammonium) : The substance (salt or mixture) when heated with NaOH solution evolves ammonia.
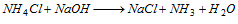
When a rod dipped in HCl is brought on the mouth of the test tube, white fumes of ammonium chloride are formed, 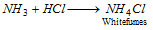
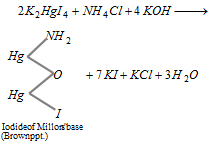
To the aqueous solution of ammonium salt when Nessler's reagents is added, brown coloured precipitate is formed.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Qualitative Analysis-Wet test for Basic Radicals questions? Qualitative Analysis-Wet test for Basic Radicals topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Qualitative Analysis-Wet test for Basic Radicals related problems. We provide step by step Qualitative Analysis-Wet test for Basic Radicals question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Qualitative Analysis-Wet test for Basic Radicals topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours