Preliminary tests
(i) Physical examination : It involves the study of colour, smell, density etc.
Table: Colour
|
Colour
|
Salt
|
|
Black
|
Oxides : MnO2,FeO,CuO,Co3O4,NiO3
Sulphides : Ag2S,CuS,Cu2S,FeS,CoS,NiS,PbS,HgS,Bi2S3 (blackish brown)
|
|
Blue
|
Hydrated CuSO4, anhydrous CaSO4
|
|
Orange
|
KO2, some dichromate K2Cr2O7 ferricyanides
|
|
Green
|
Nickel salts, hydrated ferrous salts, potassium permanganate (KMnO4), some copper (II) salts
|
|
Brownish yellow
|
SnS
|
|
Dark brown
|
PbO2, Ag2O,CdO,Fe2O3,CuCrO4,FeCl3 (but yellow in aq. solution)
|
|
Pale brown
|
MnO3
|
|
Light pink
|
Hydrated manganese salts
|
|
Reddish pink
|
Hydrated cobalt (II) salts
|
|
Red
|
HgI2.Pb3O4
|
|
Yellow
|
CdS,PbI2,AgBr,AgI chromates
|
(ii) Dry heating : Substance is heated in a dry test tube.
Table
|
Observation
|
Result
|
|
(a) A gas or vapour is evolved.
|
Compounds with water of crystallisation
|
|
|
Vapour, evolved, test with litmus paper.
|
Ammonium salts, acid salts, and hydroxides. (usually accompanied by change of colour)
|
|
|
The vapour is alkaline.
|
Ammonium substances.
|
|
|
The vapour is acidic.
|
Readily decomposable salts of strong acids.
|
|
|
Oxygen is evolved
|
Nitrates,chlorates and certain oxides.
|
|
|
Dinitrogen oxide
|
Ammonium nitrate or nitrate mixed with an ammonium salt.
|
|
|
Dark-brown or reddish fumes (oxides of nitrogen), acidic in reaction.
|
Nitrates and nitrites of heavy metals.
|
|
|
CO2is evolved, lime water becomes turbid.
|
Carbonates or hydrogen carbonates.
|
|
|
NH3is evolved which turns red litmus blue.
|
Ammonium salts.
|
|
|
SO2is evolved, which turns acidified K2Cr2O7 green, decolourises fuschin colour.
|
Sulphates and thiosulphates.
|
|
|
H2S is evolved, turns lead acetate paper black, or cadmium acetate yellow.
|
Hydrates, sulphides or sulphides in the presence of water.
|
|
|
Cl2is evolved, yellowish green gas, bleaches litmus paper, turns KI - starch blue, poisonous.
|
Unstable chlorides e.g., copper chlorides in the presence of oxidising agents.
|
|
|
Br2is evolved (reddish brown, turns fluorescent paper red).
|
Bromides in the presence of oxidising agents.
|
|
|
I2 is evolved, violet vapours condensing to black crystals
|
Free iodine and certain iodides
|
|
|
(b) A sublimate is formed
|
Ammonium and mercury salts.
|
|
|
White sublimate
|
As2O3,Sb2O3
|
|
|
Grey sublimate
|
Hg
|
|
|
Steel grey, garlic odour
|
As
|
|
|
Yellow sublimate
|
S, As2O3, HgI2(Red)S
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Characteristic flame colour : Certain metals and their salts impart specific colours to Bunsen burner flame.
(a) Pb imparts pale greenish colour to the flame.
(b) Cu and Cu salts impart blue or green colour to the flame.
(c) Borates also impart green colour to the flame.
(d) Ba and its salts impart apple green colour to the flame.
(e) Sr imparts crimson red colour to the flame.
(f) Ca imparts brick red colour to the flame.
(g) Na imparts yellow colour to the flame.
(h) K imparts pink-violet (Lilac) colour to the flame.
(i) Li imparts crimson-red, Rb imparts violet and Cs imparts violet colours to the flame.
(j) Livid- blue flame is given by As, Sb and Bi.
(iv) Borax bead test : The transparent glassy bead when heated with inorganic salt and the colour produced gives some idea of cation present in it.
Table
|
Colour of bead in oxidising flame
|
Colour of bead in reducing flame
|
Basic radical present
|
|
Greenish when hot, blue in cold.
|
Red and opaque
|
Cu
|
|
Dark green in hot and cold
|
Same
|
Cr
|
|
Deep - blue
|
Deep blue
|
Co
|
|
Yellow when hot
|
Green
|
Fe
|
|
Violet in hot and cold
|
Colourless
|
Mn
|
|
Brown in cold
|
Grey or black or opaque
|
Ni
|
Microcosmic salt bead test : Microcosmic salt, Na(NH4)HPO4.4H2O is also used to identify certain cations just as borax. When microcosmic salt is burned in a loop of platinum wire, a colourless transparent bead of sodium metaphosphate is formed.
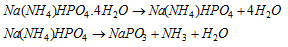
Now NaPO3 reacts with metallic oxides to give coloured orthophosphates.
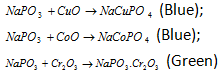
(v) Charcoal cavity test
Table :
|
(a) Compound fused in cavity directly
|
|
Nature and colour of bead
|
Cation
|
|
Yellow, brittle bead
|
Bi3+
|
|
Yellow, soft bead which marks on paper
|
Pb2+
|
|
White, brittle
|
Sb3+
|
|
White yellow when hot
|
ZnO
|
|
White garlic odour
|
As2O3
|
|
Brown
|
CdO
|
|
Grey metallic molecules attracted by magnet
|
Fe, Ni, CO
|
|
Maleable beads
|
Ag and Sn (White), Cu (Red flakes)
|
(b) Compound mixed with Na2CO3 Crystalline

Substance infusible, perform test (a)
(vi) Cobalt Nitrate test
Table:
|
Colour
|
Composition
|
Result
|
|
Blue residue
|
CaO.Al2O3
|
Al
|
|
Green residue
|
CaO.ZnO
|
ZnO
|
|
Pink dirty residue
|
CaO.MgO
|
MgO
|
|
Blue residue
|
NaCaPO4
|
PO43- in absence of Al.
|
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Qualitative Analysis of inorganic salts-Preliminary tests questions? Qualitative Analysis of inorganic salts-Preliminary tests topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Qualitative Analysis of inorganic salts-Preliminary tests related problems. We provide step by step Qualitative Analysis of inorganic salts-Preliminary tests question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Qualitative Analysis of inorganic salts-Preliminary tests topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours