Proton (1H1, H+, P)
(1) Proton was discovered by the scientist named Goldstein and proton is positively charged particle. It is a component particle of the anode rays.
(2) Goldstein (1886) had used perforated cathode in the discharge tube and repeated the experiment performed by Thomson's and observed the formation of the anode rays. These rays also known as positive or canal rays.
(3) Properties of anode rays are stated as follows
(i) Anode rays also travel in the straight line.
(ii) Anode rays are the material particles.
(iii) Anode rays are the positively charged in nature.
Table : 2.1 Comparison of the mass, charge and the specific charge of electron, proton and neutron
Name of constant
|
Unit
|
Electron(e-)
|
Proton(p+)
|
Neutron(n)
|
|
Mass (m)
|
Amu
Kg
Relative
|
0.000546
9.109 × 10-31
1/1837
|
1.00728
1.673 × 10-27
1
|
1.00899
1.675 × 10-27
1
|
|
Charge(e)
|
Coulomb (C)
Esu
Relative
|
- 1.602 × 10-19
- 4.8 × 10-10
- 1
|
+1.602 × 10-19
+4.8 × 10-10
+1
|
Zero
Zero
Zero
|
|
Specific charge (e/m)
|
C/g
|
1.76 × 108
|
9.58 × 104
|
Zero
|
|
Density
|
Gram / cc
|
2.17 * 10-17
|
1.114 * 1014
|
1.5 * 10-14
|
Table : 2.2 Other non fundamental particles
|
Particle
|
Symbol
|
Nature
|
Charge esu
´10-10
|
Mass
(amu)
|
Discovered by
|
|
Positron
|
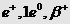 |
+
|
+ 4.8029
|
0.0005486
|
Anderson (1932)
|
|
Neutrino
|
v
|
0
|
0
|
< 0.00002
|
Pauli (1933) and Fermi (1934)
|
|
Anti-proton
|
p- |
-
|
- 4.8029
|
1.00787
|
Chamberlain Sugri (1956) and Weighland (1955)
|
|
Positive mu meson
|
µ+
|
+
|
+ 4.8029
|
0.1152
|
Yukawa (1935)
|
|
Negative mu meson
|
µ- |
-
|
- 4.8029
|
0.1152
|
Anderson (1937)
|
|
Positive pi meson
|
∏+ |
+
|
+ 4.8029
|
0.1514
|
Powell (1947)
|
|
Negative pi meson
|
∏- |
-
|
- 4.8029
|
0.1514
|
|
Neutral pi meson
|
∏0 |
0
|
0
|
0.1454
|
(iv) Anode rays might get deflected by the external magnetic field.
(v) Anode rays also affects the photographic plate.
(vi) The e/m ratio of these rays is smaller than that of the electrons.
(vii) Unlike cathode rays, their e/m value is relied upon the nature of the gas taken in the tube. It is maximum when the gas present in the tube is hydrogen.
(viii) These rays produce the flashes of light on the screen of ZnS.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Proton questions? Proton topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Proton related problems. We provide step by step Proton question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Proton topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours