Measurable properties of the gases
(1) The characteristics of the gases are described fully in terms of the four parameters or measurable properties :
(i) The volume, V, of gas.
(ii) Its pressure which is given by, P
(iii) Its temperature which is given by, T
(iv) The amount of the gas (that is the mass or number of the moles).
(2) Volume :
(i) Since the gases occupy entire space available to them, the measurement of volume of a gas only requires a measurement of the container confining the gas.
(ii) Volume is expressed in litres (L), millilitres (mL) or cubic centimeters (cm3) or cubic metres (m3).
(iii)1L = 1000mL; 1 mL = 10-3L; 1L = 1dm3 = 10-3m3
1m3 = 103 dm3 = 106 cm3 = 106 mL = 103 L
(3) Mass : (i) The mass of a gas can be determined by weighing the container in which the gas is enclosed and again weighing the container after removing gas from it. Difference between the two weights gives the mass of the gas.
(ii Mass of the gas is related to number of moles of the gas that is
moles of gas (n) = Mass in Grams/ Molar mass = m/M
(4) Temperature :
(i) Gases expand on increasing the temperature. If the temperature is increased twice, the square of the velocity (v2) also increases two times.
(ii) Temperature is measured in centigrade degree (oC) or celsius degree with the help of thermometers. The temperature can also be measured in Fahrenheit (Fo).
(iii) S.I. unit of temperature is kelvin (K) or absolute degree.
K = oC + 273
(iv) Relation between F and oC is 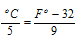
(5) Pressure : (i) Pressure of the gas is the force exerted by the gas per unit area of the walls of the container in all the directions. Therefore, Pressure (P) 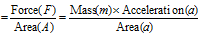
(ii) The pressure exerted by a gas is due to kinetic energy (KE =1/2 mv2) of the molecules. The Kinetic energy of the gas molecules increases, when the temperature of gas is increased. Therefore, Pressure of a gas µ Temperature (T).
(iii) The pressure of a pure gas can be measured by manometer while that of a mixture of gases by barometer.
(iv) Generally two types of the manometers are taken in use,
(a) The Open end manometer;
(b) The Closed end manometer
(v) The S.I. unit of the pressure, which is pascal (Pa), can be defined as 1 newton per metre square. It is quite small unit.
1 Pa = 1Nm-2 = 1 Kg m-1s-2
(vi) C.G.S. unit of pressure is dynes cm-2.
(vii) M.K.S. unit of pressure is kgf/m2. The unit kgf/cm2 sometime called ata (atmosphere technical absolute).
(viii) Higher unit of pressure is the bar, MPa or KPa.
1 bar = 105 Pa = 105 Nm-2 = 100KNm-2 = 100 Kpa
(ix) The several other units used for the pressure are,
|
Name
|
Symbol
|
Value
|
|
bar
|
bar
|
1 bar = 105 Pa
|
|
atmosphere
|
atm
|
1 atm = 1.01325 * 105 Pa
|
|
Torr
|
Torr
|
1 Torr = 101325/760Pa = 133.322 Pa
|
|
millimetre of mercury
|
mm Hg
|
1 mm Hg = 133.322 Pa
|
(x) The pressure relative to atmosphere is called as gauge pressure. The pressure relative to perfect vacuum is called as absolute pressure.
Absolute pressure = Gauge pressure + Atmosphere pressure.
(xi) When pressure in the system is less than the atmospheric pressure, the gauge pressure becomes negative in nature, but is frequently designated and called as vacuum. For instance, 16 cm vacuum will be
Condition
|
T
|
P
|
Vm (Molar volume)
|
|
S.T.P./N.T.P.
|
273.15 K
|
1 atm
|
22.414 L
|
|
S.A.T.P*.
|
298.15 K
|
1 bar
|
24.800 L
|
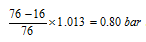
(xii) If h is height of the fluid in the column or difference in the heights of the fluid columns in the two limbs of manometer, d is the density of the fluid (hg = 13.6 * 103 kg/m3 = 13.6 g/cm3) and g is gravity, then pressure can be given by, Pgas = Patm + hdg
(xiii) Two sets of the conditions are widely used as 'standard' values for reporting the data.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Properties of Gas questions? Properties of Gas topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Properties of Gas related problems. We provide step by step Properties of Gas question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Properties of Gas topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours