Power: It is described as rate of work done with respect to time. There are two kinds of power:
(i) Rate of doing work is known power. It is a scalar quantity. If velocity vector creates an angle θ with the force component, then 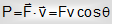
(ii) In rotator motion: 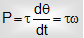
Since P=dW/dt
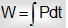 Therefore area inside power-time graph is same to work done.
Therefore area inside power-time graph is same to work done.
Average Power
In a given interval of time it is described as net work divided by net time.
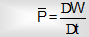
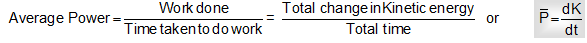
Instantaneous Power (P)
The instantaneous power of an agent is described as the limiting value of the average power of an agent in a small time interval, when the time interval tends to zero.
Thus, if DW is work done in a small interval D t, then instantaneous power is shown as
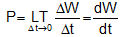 ... (i)
... (i)
Now, 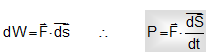
Again,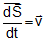 , the instantaneous velocity of the particle. Therefore,
, the instantaneous velocity of the particle. Therefore, 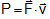 ... (ii)
... (ii)
Thus, instantaneous power of an agent is calculated as the dot product of its instantaneous velocity and the force acting on it at that instant.
If θ is angle between and , then P = F v cosθ
In caseθ = 0o, P = F v
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Power questions? Power topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Power related problems. We provide step by step Power question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Power topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours