Oxidising and Reducing agents
(1) Definition : The substance (atom, ion or molecule) that gains electrons and is thereby reduced to a low valency state is called an oxidising agent, while substance which loses electrons and is thereby oxidised to the higher valency state is called a reducing agent.
Or
The oxidising agent is a substance, whose oxidation number of atom decreases while a reducing agent is a substance the oxidation number of whose atom increases.
(2) Important oxidising agents are as follows
(i) Molecules made up of the electronegative elements.
Such as : O2, O3 and X2 (halogens).
(ii) The compounds containing the element which is in the highest oxidation state.
Example : KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, Na2Cr2O7, CrO3, H2SO4
HNO3, NaNO3, FeCl3, HgCl2, KClO4, SO3, CO2, H2O2 etc.
(iii) Oxides of elements, MgO, CuO, CrO3, CO2, P4O10 etc.
(iv) Fluorine is strongest oxidising agent.
(3) Important reducing agents
(i) All metals for example Fe, Na, Al Zn, , etc.
(ii) A few non-metals for example C, H2, S etc.
(iii) Hydracids : HCl, HBr, HI, H2S etc.
(iv) Few compounds containing an element in lower oxidation state (ous).
Example : FeCl2, FeSO4, SnCl2, Hg2Cl2, Cu2O etc.
(v) Metallic hydrides e.g. NaH, LiH etc.
(vi) Organic compounds such as HCOOH and (COOH)2 and their salts, , alkanes aldehydes etc.
(vii) Lithium is strongest reducing agent in the solution.
(viii) Cesium is the strongest reducing agent in absence of water. Other reducing agents are Na2S2O3 and KI.
(ix) Hypo prefix indicates that central atom of compound has the minimum oxidation state so it will act as a reducing agent.
Example : H3PO2 (hypophosphorous acid).
(4) The Substances which act as oxidising as well as reducing agents
Examples : H2O2,SO2,H2SO3,HNO2,NaNO2,Na2SO3,O3 etc.
(5) Tips for identification of the oxidising and reducing agents
(i) If the element is in its highest possible oxidation state in the compound, compound can function as an oxidising agent.
Example :KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4 etc.
(ii) If the element is in its lowest possible oxidation state in a compound, the compound can function only as a reducing agent.
Example : H2S, H2C2O4, FeSO4, Na2S2O3, SnCl2 etc.
(iii) If the element is in its intermediate oxidation state in a compound, the compound can function both as an oxidising agent as well as reducing agent.
Example : H2O2, H2SO3, HNO2, SO2 etc.
(iv) If the highly electronegative element is in its highest oxidation state in a compound, that compound can function as a powerful oxidising agent.
Example : KClO4, KClO3, KBrO3, KIO3 etc.
(v) If the electronegative element is in its lowest possible oxidation state in a compound or in free state, it can function as a powerful reducing agent.
Example : I-, Br-, N3- etc.
(6) Equivalent weight of oxidising and reducing agents
Equivalent weight of a substance (oxidant or reductant) is equal to molecular weight divided by number of electrons lost or gained by one molecule of the substance in a redox reaction.
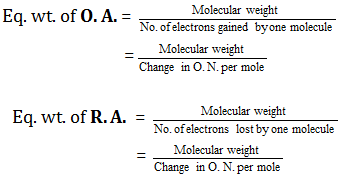
Table: Equivalent weight of few oxidising/reducing agents
|
Agents
|
O. N.
|
Product
|
O. N.
|
Change in
O. N. per
atom
|
Total
Change in
O. N. per mole
|
Eq. wt.
|
|
Cr2O72-
|
+ 6
|
Cr3+
|
+ 3
|
3
|
3 × 2 = 6
|
Mol. wt./6
|
|
C2O42-
|
+ 3
|
CO2
|
+ 4
|
1
|
1 × 2 = 2
|
Mol. wt./2
|
|
S2O32-
|
+ 2
|
S4O62-
|
+ 2.5
|
0.5
|
0.5 × 2 = 1
|
Mol. wt./1
|
|
H2O2
|
- 1
|
H2O
|
- 2
|
1
|
1 × 2 = 2
|
Mol. wt./2
|
|
H2O2
|
- 1
|
O2
|
0
|
1
|
1 × 2 = 2
|
Mol. wt./2
|
|
MnO4-
(Acidic medium)
|
+ 7
|
Mn2+
|
+ 2
|
5
|
5 × 1 = 5
|
Mol. wt./5
|
|
MnO4-
(Neutral medium)
|
+ 7
|
MnO2
|
+ 4
|
3
|
3 × 1 = 3
|
Mol. wt./3
|
|
MnO4-
(Alkaline medium)
|
+ 7
|
MnO42-
|
+ 6
|
1
|
1 × 1 = 1
|
Mol. wt./1
|
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Oxidising and Reducing Agents questions? Oxidising and Reducing Agents topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Oxidising and Reducing Agents related problems. We provide step by step Oxidising and Reducing Agents question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Oxidising and Reducing Agents topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours