Some other periodic properties
(1) Atomic volume : It is defined as the volume occupied by one gram atom of an element. The formula of it can be described as follows,
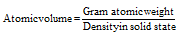
Units of atomic volume are cc/mole. The atomic volume signifies the volume occupied by one mole (Avogadro number) of atoms of the given element in solid state. The lower atomic volume usually leads to increased hardness, higher density, and brittleness, less malleability, higher melting and boiling points, and lesser ductility.
(i) While descending the group, atomic volume usually increases which is due to increase in the number of shells though the valence electrons in a given group remains constant.
(ii) While moving from left to right across the period the atomic volume first decreases to a minimum and then increases. The metal francium has the highest atomic volume and boron has lowest atomic volume.
(2) Density : The density of the elements in solid state varies periodically with their atomic numbers. In the beginning the density increases gradually in the period and becomes maximum somewhere for the central members and then starts decreasing afterwards gradually.
(3) Melting and boiling points : The melting points of the elements exhibit some periodicity with rise of atomic number. It is seen that elements with low values of atomic volumes have high melting points while elements with high values of atomic volumes have low melting points. Generally, melting points of elements in any periodic at first increase and become maximum somewhere in the centre and thereafter begins to decreases.
Tungsten has the maximum melting point (3410°C) amongst metals and carbon has the maximum melting point (3727°C) amongst non-metals. Helium has the minimum melting point (-270°C). The metals, Cs, Ga and Hg are known in liquid state at 30°C.
Boiling points of the elements also show almost similar trends, however, the regularities are not so striking as noted in the case of melting points.
(4) Oxidation state ( also known as Oxidation number, O.N.) : Oxidation number of an element in a compound is the total number of electrons it appears to have gained or lost (negative and positive oxidation states respectively) during the formation of that particular compound.
Note : For detail see chapter redox reaction. (5) Magnetic properties : Magnetic properties of matter depend on the properties of the individual atoms. A substance (atom, ion or compound) capable of being attracted into a magnetic field is known as paramagnetic. Paramagnetic substances posses a net magnetic moment which in turn is due to the presence of unpaired electron(s) in atoms, ions or molecules. As most of the transition metal ions posses unpaired d-electrons, they show paramagnetic behaviour. The exceptions are Sc3+, Ti4+, Zn2+, Cu+ etc. which do not contain any unpaired electron and hence are diamagnetic.
On the other hand, a substance which is repelled by a magnetic field is known as diamagnetic. This type of substances do not have any net magnetic moment because they do not have any unpaired electron. The electrons determines magnetic properties of the matter in two ways,
- Each electron can be treated as a small sphere of negative charge spinning on its axis. Spinning of the charge produces magnetic moment.
- The electron moving in the closed path around a nucleus will also produce magnetic moment just as does electric current travelling in a loop of wire.
The observed magnetic moment is therefore the sum of the two moments: the spin moment and the orbital moment. It can be expressed in units called Bohr Magnetons (BM). In terms of n (number of unpaired electron), magnetic moment can be calculated by the formula 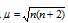
Larger the number of unpaired electrons in a substance, the larger is the magnetic moment of the substance. Value of the magnetic moment has been used to calculate the number of unpaired electrons in an ion. In some of the cases, even structure of the molecule or complex is indicated by its magnetic moment.
Paramagnetism is generally measured by a simple device known as Guoy's balance which involves weighing the species in presence of a magnetic field.
Ferromagnetism is a special property observed in some of the substances in the solid state. This type of substances is strongly attracted to magnetic field and may retain the magnetic properties for some time even after the removal of the field. The most frequent example is of Fe followed by Co and Ni.
(6) Hydration and hydration energy
(i) Hydration energy can be described as the enthalpy change that accompanies the dissolving of 1 mol of gaseous ions in water.
(ii) Size of ions and its charge determines extent of hydration. Larger the charge smaller the size of the ion, larger the attraction for the lone pair of O of H2O, hence greater the extent of hydration energy.
(a) The size of hydration ion increases.
(b) Ionic mobility decreases i.e. heavier (hydrated) ions moves slower.
(7) Acid-base-character of oxides
(i) On going across a period, basic character of the oxides gradually changes first into amphoteric and finally into acidic character.
(ii) On going down the group, reverse behaviour is observed that is from more acidic to more basic.
(iii) Stability of the oxides decreases across a period.
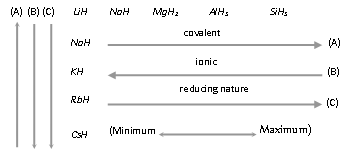
(8) Hydrides
(i) The hydrogen combines with the number of other elements including metals and non-metals to form compounds called hydrides.
(ii) The covalent nature of hydrides increases across a period and decreases down the group.
(iii) The ionic hydride are better reducing agents than the covalent hydride and reducing nature of hydride decreases across the period and increases down the group.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Other periodic properties questions? Other periodic properties topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Other periodic properties related problems. We provide step by step Other periodic properties question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Other periodic properties topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours