Ostwald's dilution law
The strength of an acid or a base is experimentally measured by determining the dissociation or ionisation constant.
When acetic acid (a weak electrolyte) is dissolved in water, it dissociates partially into H+ or H3O+ and CH3COO- ions and the following equilibrium is obtained,
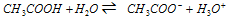
Applying law of chemical equilibrium,
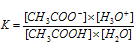
In dilute solution, [H2O] is constant. The product of K and constant [H2O] is denoted as Ka, the ionization constant or dissociation constant of the acid is,
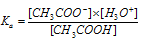 .....(i)
.....(i)
The fraction of the total amount of molecules of an electrolyte which ionise into the ions is called as degree of dissociation/ionisation α.
If 'C' represents the initial concentration of the acid in moles L-1 and α degree of dissociation, then the equilibrium concentration of ions (CH3COO- and H3O+) is equal to the Cα and that of the undissociated acetic acid
= C(1-α) i.e., we have
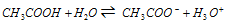
Initial conc C 0 0
Conc. at eqb. C(1-α) Cα Cα
Putting the values of the equilibrium concentrations in equation one we get
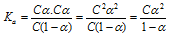 .....(ii)
.....(ii)
In case of weak electrolytes, the value of α is very small and can be neglected in comparison to 1 which means 1- α = 1.
Hence, we obtain
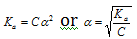 .....(iii)
.....(iii)
The degree of dissociation, α can therefore be calcualted at a given concentration, C if Ka is known. Furher, if V is the volume of the solution in litres containing 1 mole of the electrolyte, C=1/V. Hence we have
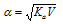 .....(iv)
.....(iv)
Similarly, for a weak base like NH4OH, we have
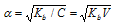 .....(v)
.....(v)
The equations given above lead to the following result
"For a weak electrolyte, the degree of ionisation is inversely proportional to the square root of molar concentration or directly proportional to the square root of volume containing one mole of the solute."
This is called Ostwald's dilution law.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Ostwald's dilution law questions? Ostwald's dilution law topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Ostwald's dilution law related problems. We provide step by step Ostwald's dilution law question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Ostwald's dilution law topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours