The nuclei have been divided on the basis of the number of protons (atomic number) or the total number of nucleons (mass number) as follows
(i) Isotopes: The atoms of element having same atomic number but different mass number are known as isotopes. All isotopes have the similar chemical properties. The isotopes of similar components are the following
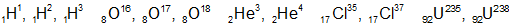
(ii) Isobars: The nuclei which have the same mass number (A) but different atomic number (Z) are called isobars. Isobars occupy different positions in periodic table so all isobars have different chemical characteristics. Some of the types of isobars are
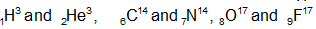
(iii) Isotones: The nuclei having equal number of neutrons are called isotones. For them both the atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) are different, but the value of (A - Z) is same. Some examples are
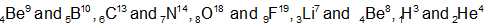
(iv) Mirror nuclei: Nuclei having the same mass number A but with the proton number (Z) and neutron number (A - Z) interchanged (or whose atomic number differ by 1) are called mirror nuclei for example.
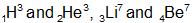
Size of nucleus:
(i) Nuclear radius: Experimental results indicate that the nuclear radius is related to A1/3, where A is the volume number of nucleus i.e. 
(ii) Nuclear volume: The mass of nucleus is shown by 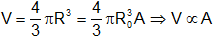
(iii) Nuclear density: Volume per unit mass of a nucleus is called nuclear density.
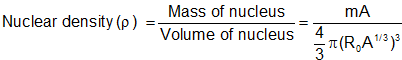
where m = Average of mass of a nucleon (= mass of proton + mass of neutron = 1.66 * 10-27 kg) and mA = Mass of nucleus
Pair production and pair-annihilation:
|
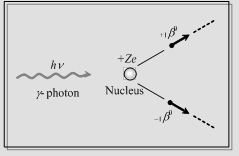
When an energetic y-ray photon falls on a heavy materials. It is absorbed by few atoms of the substance and an electron and a positron are given. This process is known as pair production and may be represented by the following equation
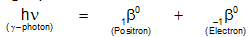
|
|
The rest-mass power of every of positron and electron is
E0 = m0c2 = (9.1 * 10-31 kg) * (3.0 * 108 m/s)2
= 8.2 * 10-14 J = 0.51 MeV
Hence, for pair-production it is essential that the energy of g-photon must be at least 2 ´ 0.51 = 1.02 MeV. If the energy of g-photon is less than this, it would create problem photo-electric effect or Compton Effect on striking the matter.
The converse phenomenon pair-annihilation is also possible. Whenever an electron and a positron get very close to one another, they annihilate one another by combining together and two g-photons (energy) are given. This process is known as pair annihilation and is represented by the following equation.
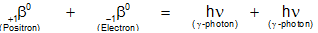
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Nucleus questions? Nucleus topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Nucleus related problems. We provide step by step Nucleus question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Nucleus topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours