Molecular collisions
(1) The closest distance between the centres of the two molecules taking part in the collision is called as molecular or collision diameter (s). The molecular diameter of all the gases is nearly same lying in order of 10-8 cm.
(2) Number of the collisions taking place in the unit time per unit volume, called as collision frequency (z).
(i) The number of collision made by the single molecule with other molecules per unit time can be given by, 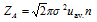
here n is the number of molecules per unit molar volume, 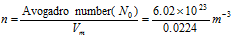
(ii) The total number of bimolecular collision per unit time are given by, 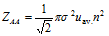
(iii) If the collisions involve two different molecules, the number of bimolecular collision can be given by,
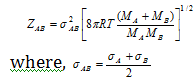
MA, MB are molecular weights (M = mNo)
(iv) (a) At particular temperature; 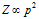
(b) At particular pressure; 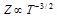
(c) At particular volume; 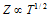
(3) During molecular collisions the molecule covers a small distance before it gets deflected from it path. The average distance travelled by gas molecules between the two successive collisions is called as mean free path (λ).
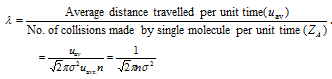
(4) Based on the kinetic theory of the gases mean free path, 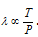 . Therefore we can say that
. Therefore we can say that
(i) Larger the size of molecules, smaller the mean free path, which gives 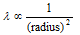
(ii) The greater number of molecules per unit volume, the smaller will be mean free path.
(iii) Larger the temperature, larger will be the mean free path.
(iv) Larger the pressure, smaller will be the mean free path.
(5) Relation between the collision frequency (Z) and the mean free path ( λ ) can be given by, 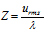
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Molecular collisions questions? Molecular collisions topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Molecular collisions related problems. We provide step by step Molecular collisions question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Molecular collisions topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours