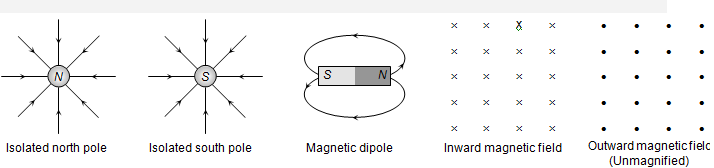
(1) Magnetic field and magnetic lines of force : Space around a magnetic pole or magnet or current carrying wire within which it's effect can be experienced is defined magnetic field. Magnetic field may be presented with the help of a set of lines or curves called magnetic lines of force.
(2) Magnetic flux (Φ) and flux density (B)
(i) The number of magnetic lines of force passing normally through a surface is defined as magnetic flux (f). It's S.I. unit is weber (wb) and CGS unit is Maxwell.
Remeber 1 wb = 108 maxwell.
|
(ii) When a piece of a magnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field the substance converts into magnetised. The number of magnetic lines of induction inside a magnetised substance crossing unit area normal to their direction is called magnetic induction or magnetic flux density It is a vector quantity.
|
|
It's SI unit is Tesla which is same to 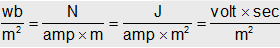
and CGS unit is Gauss. Remember 1 Tesla = 104 Gauss.
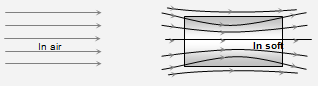
(3) Magnetic permeability: It is the degree or extent to which magnetic lines of force can enter a substance and is denoted by μ. OR
|
Characteristic of a medium which allows magnetic flux to pass through it is called it's permeability. e.g. permeability of hard iron is 1000 times greater than that of air.
Also μ = where absolute permeability of air or free space =
|
|
and Related permeability of the medium = 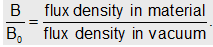
(4) Intensity of magnetizing field (magnetizing field) : It is the degree or extent to which a magnetic field can magnetism a atom. Also H = B/μ.
It's SI unit is 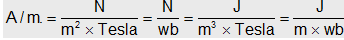 It's CGS unit is Oersted. Also 1oersted = 80 A/m
It's CGS unit is Oersted. Also 1oersted = 80 A/m
(5) Intensity of magnetization (I) : It is the degree to which a substance is magnetized when placed in a magnetic field.
It can also be defined as the pole strength per unit cross sectional area of the substance or the induced dipole moment per unit volume.
Hence I=m/A It is a vector value, its S.I. unit is Amp/m.
(6) Magnetic susceptibility (cm) : It is the property of the substance which shows how easily a substance can be magnetized. It may also be described as the ratio of intensity of magnetization (I) in a substance to the magnetic intensity (H) applied to the substance, i.e.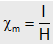 . It is a scalar quantity with no units and dimensions.
. It is a scalar quantity with no units and dimensions.
7) Relation between permeability and susceptibility: Total magnetic flux density B in a material is the sum of magnetic flux density in vacuum produced by magnetizing force and magnetic flux density due to magnetization of material . i.e.
=> 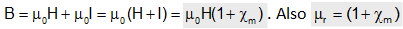
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Magnetic field, flux and density questions? Magnetic field, flux and density topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Magnetic field, flux and density related problems. We provide step by step Magnetic field, flux and density question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Magnetic field, flux and density topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours