Lowering of the vapour pressure
The quantity of pressure exerted by the vapours over the liquid surface in the equilibrium with the liquid at the given temperature is known as vapour pressure of the liquid. The vapour pressure of the liquid depends on the following properties,
(1) Nature of liquid : The liquids, which posses the weak intermolecular forces, are volatile in nature and have greater vapour pressure. For instance, dimethyl ether has greater vapour pressure than the ethyl alcohol.
(2) Temperature : The vapour pressure increases with increase in temperature. This is due to the reason that with the increase in temperature more molecules of liquid can go into the vapour phase.
(3) Purity of the liquid : The pure liquid always has the vapour pressure greater than its solution.
Raoult's law : It states that when the non-volatile substance is dissolved in the liquid, the vapour pressure of the liquid (or solvent) is lowered. According to Raoult's law (in the year 1887), at any given temperature the partial vapour pressure (pA) of any component of the solution is equal to its mole fraction (XA) multiplied by vapour pressure of this component in the pure state P0A. Which means, PA = P0A * XA
Vapour pressure of the solution PTotal is the sum of the partial pressures of the components, that is for the solution of two volatile liquids with vapour pressures PA and PB.
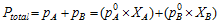
On the other hand, Raoult's law can be stated as the relative lowering of the vapour pressure of a solution containing the non-volatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of the solute in the solution.
The relative lowering of vapour pressure is defined as ratio of lowering of vapour pressure to the vapour pressure of pure solvent. It is determined by the Ostwald-Walker method.
Therefore according to Raoult's law,
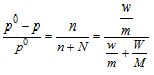
here, p= The vapour pressure of solution
P0Vapour pressure of the pure solvent
n= Number of moles of the solute
N= Number of moles of the solvent
w and m= weight and mol. wt. of solute
W and M weight and mol. wt. of the solvent.
Limitations of the Raoult's law
- The Raoult's law is applicable only to the very dilute solutions.
· The Raoult's law is valid to solutions containing non-volatile solute only.
· The Raoult's law is not applicable to the solutes which dissociate or associate in particular solution.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Lowering of Vapour Pressure or Raoult's Law questions? Lowering of Vapour Pressure or Raoult's Law topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Lowering of Vapour Pressure or Raoult's Law related problems. We provide step by step Lowering of Vapour Pressure or Raoult's Law question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Lowering of Vapour Pressure or Raoult's Law topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours