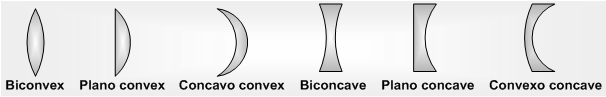
(i) Lens is a transparent medium bounded by two refracting surface, such as at least one field is curved. Curved surface may be cylindrical, spherical etc.
(ii) Lenses are of two basic kinds convex which are thicker in the middle than at the edges and concave for which the reverse holds.
(iii) Principal focus : We define two principal focus for the lens. We are primarily consider with the second principal focus (F). Thus wherever we show the focus, it seems the second principal focus.
First principal focus : An object point for which image is formed at infinity.

Second principal focus : An image point for an object at infinity.
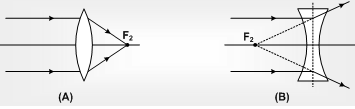
Focal length (f) : Distance of second principal focus from optical centre is called focal length
fconvex → positive fconcave → negative, fplane = 0
Aperture : Effective diameter of light transmitting area is called aperture. Intensity of image μ (Aperture)2
Power of lens (P) : Means the ability of a lens to deviate the path of the rays going through it. If the lens converges the waves parallel to the principal axis its power is positive and if it diverges the rays it is negative.
Power of lens P = 1/f(m) = 100/f(cm); Unit of power is Diopter (D)
Pconvex = positive, Pconcave = negative, pplane = zero.
Lens Maker's Formula and Lens Formula:
Lens maker's formula: If R1 and R2 are the radii of curvature of first and second refracting surfaces of a thin lens of focal length f and refractive index (w.r.t. surrounding medium) then the relation between f, , R1 and R2 is known as lens maker's formula.
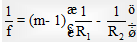
Lens formula: The relation which denotes the relation between u, v and f is called lens formula. 1/f = 1/v - 1/u
Magnification:
The ratio of the size of the picture to the size of body is known magnification.
(i) Transverse magnification: 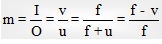 (use sign convention while solving the problem)
(use sign convention while solving the problem)
(ii) Longitudinal magnification : 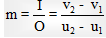 For very small object
For very small object 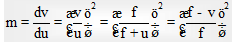
(iii) Areal magnification : 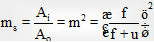
( Ai = Area of image, A0 = Area of object)
Relation between image speed and object: If an object moves with constant speed (v0) towards a convex lens from infinity to focus, the image will move slower in the beginning and then faster.
Also 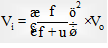
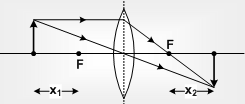
Newton's Formula:
If the distance of object (x1 ) and image (x2) are not measured from optical origin, but from first and second rule foci then Newton's formula states
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Lens questions? Lens topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Lens related problems. We provide step by step Lens question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Lens topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours