Laws of thermochemistry
(1) Levoisier and Laplace law : In accordance to this law enthalpy of decomposition of the compound is numerically equal to the enthalpy of formation of that specific compound with opposite sign,
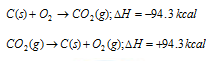
(2) Hess's law (law of the constant heat summation): This law was presented by Hess in the year 1840. According to this law If a chemical reaction can be made to take place in a number of ways in one or in several steps, the total enthalpy change (total heat change) is always the same, that is the total enthalpy change is no dependent on the intermediate steps involved in the change. Enthalpy change of a chemical reaction depends on the initial and final stages only. Assume that the substance A be changed in three steps to D with enthalpy change from A to B, ?H1 calorie, from B to C,?H2 calorie and from C to D,?H3 calorie. The total enthalpy change from A to D will be equal to sum of the enthalpies involved in various steps,
the total enthalpy change will be 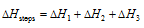
Now if D is directly converted into A, let the enthalpy change be 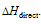 According to Hess's law
According to Hess's law 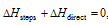 i.e.
i.e. 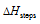 must be equal to
must be equal to 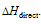 numerically but with opposite sign. In case it is not so, say
numerically but with opposite sign. In case it is not so, say 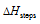 (which is negative) is more that
(which is negative) is more that 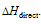 (which is positive), then will be in one cycle, some of the energy will be created which is not possible on the basis of first law of thermodynamics. Thus,
(which is positive), then will be in one cycle, some of the energy will be created which is not possible on the basis of first law of thermodynamics. Thus, 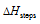 must be equal to
must be equal to 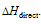 numerically.
numerically.
(i) Experimental verification of the Hess's law is as follows
(a) Formation of the carbon dioxide from carbon
First method : carbon is directly converted into CO2 (g)
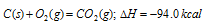
Second method : Carbon is first converted into CO (g) and then CO (g) into CO2 (g), i.e. conversion has been carried in two steps,
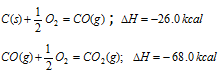
Total enthalpy change C(s) to CO2 (g) 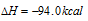
(b) Formation of the ammonium chloride from ammonia and hydrochloric acid:
First method 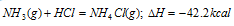
NH4Cl(g)+aq= NH4Cl(aq); DH = + 4.0 kcal
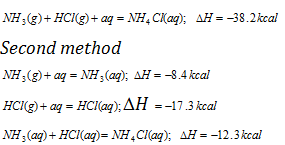
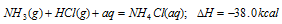
(ii) Applications of Hess's law
(a) For determination of the enthalpies of formation of those compounds which cannot be prepared directly from the elements easily using enthalpies of combustion of compounds.
(b) For the determination of enthalpies of extremely slow reactions.
(c) For determination of the enthalpies of transformation of one allotropic form into another.
(d) For determination of the bond energies.
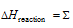 The Bond energies of reactants -the sum of Bond energies of products.
The Bond energies of reactants -the sum of Bond energies of products.
(e) For determination of the resonance energy.
(f) For determination of the lattice energy.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Laws of Thermochemistry questions? Laws of Thermochemistry topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Laws of Thermochemistry related problems. We provide step by step Laws of Thermochemistry question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Laws of Thermochemistry topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours