Laws of crystallography : The crystallography is based on the three fundamental laws which are as follows.
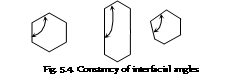
(i) The Law of constancy of the interfacial angles : This law states that angle between the adjacent corresponding faces is the inter facial angles of the crystal of the particular substance is always constant inspite of having different shapes and sizes and mode of growth of crystal. The size and shape of the crystal depend upon the conditions of the crystallisation. This law is also called as Steno's Law.
(ii) The Law of rational indices : This law describes that the ratio of intercepts of the different faces of a crystal with the three axes are constant and can be expressed by the rational numbers that the intercepts of any face of the crystal along the crystallographic axes are either equal to unit intercepts (which means intercepts made by the unit cell) a, b, c or various simple whole number multiples of them such as na, n' b, n''c, where n, n' and n'' are the simple whole numbers. The whole numbers n, n' and n'' are known as Weiss indices. This law was given by the scientist Hauy.
(iii) The Law of constancy of symmetry : In accordance to this law, all the crystals of a substance have the same elements of the symmetry is the plane of symmetry, the axis of symmetry and the centre of symmetry.
Miller indices: The planes in the crystals are described by a set of integers (such as h, k and l) known as Miller indices. The Miller indices of the plane are reciprocals of the fractional intercepts of that plane on the a variety of crystallographic axes. For calculating the Miller indices, a reference plane, generally known as parametral plane, is selected having the intercepts of a, b and c along the y,x and z-axes, respectively. Then, the intercepts of the unknown plane are given with respect to the a, b and c of parametral plane.
Therefore, the Miller indices are :
h=a/intercept of the plane along x-axia
k=b/intercept of plane along y axis
l=c/intercept of plane along z-axis
Distance between the parallel planes in the crystals are designated as dhkl. For different cubic lattices these inter planar spacing can be given with the help of general formula which is given as follows,
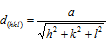
Here a is the length of side of the cube while h, k and l are the Miller indices of the plane.
Hear when the plane is parallel to the axis, its intercept with that axis is taken as infinite and the Miller will become zero.
The negative signs in Miller indices are indicated by placing the bar on the intercept. All the parallel planes have the same Miller indices.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Laws of Crystallography questions? Laws of Crystallography topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Laws of Crystallography related problems. We provide step by step Laws of Crystallography question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Laws of Crystallography topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours