Internal energy, heat and Work
(1) Internal energy (E) : Every system having some quantity of matter is associated with a definite amount of the energy. This energy is called as internal energy.
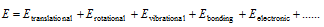
(i) Characteristics of internal energy
(a) The internal energy of a system is the extensive property.
(b) The internal energy is the state property.
(c) The change in internal energy does not depend on path by which the final state is reached.
(d) There will be no change in the internal energy in the cyclic process.
(e) The internal energy of the ideal gas is a function of temperature only.
(f) Internal energy of the system depends upon the quantity of the substance, its temperature, chemical nature, pressure and volume.
(g) The unit of E is ergs in CGS or joules in SI
1 Joule = ergs.
(ii) Change in internal energy (ΔE ) : It is neither possible nor necessary to calculate the absolute value of internal energy of a system then, ΔE = Ef - Ein ; is positive if Ef > Ein and negative if Ef < Ein.
(2) Heat (q) and work (w): The energy of a system may increase or decrease in several ways but two common ways are heat and work.
Heat is a form of energy. It flows from one system to another because of the difference in temperature between them. Heat flows from higher temperature to lower temperature. Thus, it is regarded as the energy on move.
Work is said to be performed if the point of application of force is displaced in the direction of the force. It is equal to the force multiplied by the displacement (distance through which the force acts).
There are three main types of work which we usually come across. These are electrical work Gravitational work and mechanical work.
The mechanical work = Force displacement
The Electrical work = the potential difference charge
Gravitational work = mgh
(i) Units of heat and work : The heat changes are measured in calories (cal), Kilo calories (kcal), joules (J) or kilo joules (kJ). These are related as, 1 cal = 4.184 J; 1kcal = 4.184kJ
The S.I. unit of heat is joule (J) or kilojoule. The Joule (J) is equal to Newton - metre (1 J= 1 Nm).
Work is measured in terms of ergs or joules. The SI unit of work is given by Joule.
1 Joule = 107 ergs = 0.2390 cal.
1 cal > 1 joule > 1 erg
(ii) The sign conventions for the heat and work
Heat absorbed by system = q positive
Heat evolved by system = q negative
Work done on the system = w positive
Work done by the system = w negative.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Internal energy, Heat and Work questions? Internal energy, Heat and Work topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Internal energy, Heat and Work related problems. We provide step by step Internal energy, Heat and Work question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Internal energy, Heat and Work topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours