Identities:
A sampling rate converter (the ↓M or ↑L operation) is a linear time-changing system. On the other hand, the filters Hd(z) and Hu(z) are linear time-invariant systems. Usually the order of a sampling rate converter and a linear time-invariant system msy not be interchanged. We derive below various identities, two of which are called as noble identities (viz., identities 3 and 6, all the others being special cases), which help to swap the position of a filter with that of a down- sampler or up-sampler by properly changing the filter.
Recall that the input-output description of a down-sampler is
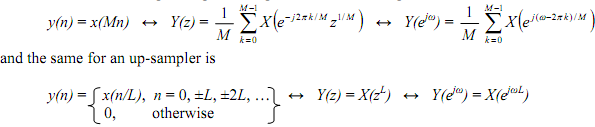
which we use in the following development.
Example Show that the given systems are equivalent.
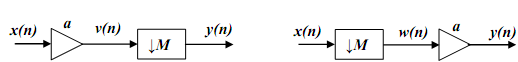
In the structure on the left the procedure of creating y(.) consists of multiplying every input sample x(.) by a and then, in the down-sampling process, dropping (M-1) of these products for every Mth one we need. The structure on the right is more efficient computationally: the (M-1)th samples are dropped first and every M is multiplied by a, that is, only the samples that are 100(M -1)/M retained are multiplied. The number of multiplications is replaced by %.
Email based Identities assignment help - Identities homework help at Expertsmind
Are you finding answers for Identities based questions? Ask Identities questions and get answers from qualified and experienced Digital signal processing tutors anytime from anywhere 24x7. We at www.expertsmind.com offer Identities assignment help -Identities homework help and Digital signal processing problem's solution with step by step procedure.
Why Expertsmind for Digital signal processing assignment help service
1. higher degree holder and experienced tutors
2. Punctuality and responsibility of work
3. Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
4. On Time Delivery
5. Privacy of information and details
6. Excellence in solving Digital signal processing queries in excels and word format.
7. Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours