Hydrogen ion concentration - pH scale
Sorensen, a Danish biochemist developed a scale to measure the acidity in terms of concentrations of H+ in a solution. As defined by the scientist, pH of the solution is negative logarithm to the base 10 of concentration of H+ ions which it contains.
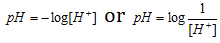
Just as pH indicates the hydrogen ion concentration, pOH represents the concentration of the hydroxyl ion, which is given by
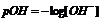
Considering the relationship, 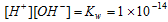
Taking log on both sides, we have
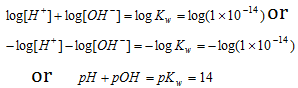
|
|
[H+]
|
[OH-]
|
pH
|
pOH
|
|
Acidic solution
|
> 10-7
|
< 10-7
|
< 7
|
> 7
|
|
Neutral solution
|
10-7
|
10-7
|
7
|
7
|
|
Basic solution
|
< 10-7
|
> 10-7
|
> 7
|
< 7
|
pH of some materials
|
Material
|
pH
|
Material
|
pH
|
|
Gastric juice
|
1.4
|
Rain water
|
6.5
|
|
Lemon juice
|
2.1
|
Pure water
|
7.0
|
|
Vinegar
|
2.9
|
Human saliva
|
7.0
|
|
Soft drinks
|
3.0
|
Blood plasma
|
7.4
|
|
Beer
|
4.5
|
Tears
|
7.4
|
|
Black coffee
|
5.0
|
Egg
|
7.8
|
|
Cow's milk
|
6.5
|
Household ammonia
|
11.9
|
The limitations of pH scale
(i) pH values of solutions do not provide us immediate idea of the relative strengths of solutions. A solution of the pH =1 has the hydrogen ion concentration 100 times that of the solution pH = 3 (not the three times). A 4 * 10-5 N HCl is twice the concentrated of a 2 * 10-5 N HCl solution, but pH values of these solutions are 4.40 and 4.70 respectively.
(ii) pH value zero is obtained in 1N solution of strong acid. If the concentration is 2N, 3N, 10N, etc. the respective pH values will be negative.
(iii) A solution of the acid having quite low concentration, say 10-8N, can not have pH 8, as shown by pH formula but the actual pH value will be less than 7.
pK value : p stands for negative logarithm. Just as H+ and OH- ion concentrations range over many negative powers of 10, it is convenient to represent them as pH or pOH, dissociation constant (as K) values also range over many negative powers of ten and it is convenient to write them as pK. Therefore, pK is negative logarithm of dissociation constant.
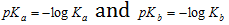
Weak acids have higher pKa values. Similarly weak bases have higher pKb values
For any conjugate acid-base pair in aqueous solution, Ka * Kb = Kw
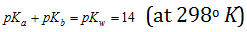
Calculation of the pH of 10-8 M HCl & 10-8 M NaOH
If we use the relation 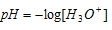 we get the pH equal to 8, but this is not accurate because an acidic solution cannot have pH greater than 7. In this condition H+concentration of water cannot be neglected.
we get the pH equal to 8, but this is not accurate because an acidic solution cannot have pH greater than 7. In this condition H+concentration of water cannot be neglected.
Therefore, 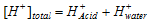
Since HCl is strong acid and completely ionised,
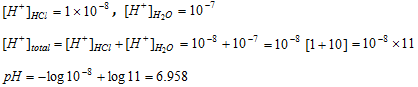
Similarly if NaOH concentration is 10-8 M
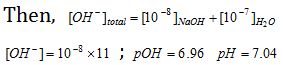
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Hydrogen ion concentration – pH scale questions? Hydrogen ion concentration – pH scale topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Hydrogen ion concentration – pH scale related problems. We provide step by step Hydrogen ion concentration – pH scale question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Hydrogen ion concentration – pH scale topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours