Heterolysis bond fission or Heterolytic
(i) In heterolysis, the covalent bond is broken in such a way that one species (i.e., less electronegative) is deprived of its own electron, while the other substance gets both the electrons.
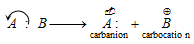
Thus formation of opposite charged particles takes place. In case of organic molecules, if positive charge is present on the carbon then cation is termed as carbocation. If negative charge is present on the carbon then anion is termed as carbanion.
(ii) The segment which favors heterolysis is greater difference of electronegativities between A and B.
(iii) Functionality of the solution in which heterolysis takes place is known as heterolytic mechanism or ionic mechanism.
(iv) The energy needs for heterolysis is usually greater than that for homolysis due to electrostatic forces of attraction between ions.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Heterolysis bond fission or Heterolytic questions? Heterolysis bond fission or Heterolytic topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Heterolysis bond fission or Heterolytic related problems. We provide step by step Heterolysis bond fission or Heterolytic question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Heterolysis bond fission or Heterolytic topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours