Heterojunction bipolar transistor
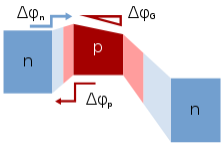
The bands in the graded heterojunction NPN bipolar transistor. Barriers indicated for the electrons to move from emitter to base, and for the holes to be injected backward from base to emitter; Also, grading of bandgap in base assists electron transport in the base region; Light colors indicate depleted regions
The heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT) is the improvement of BJT which can handle signals of quite high frequencies up to hundred GHz. It is common in the modern ultrafast circuits, mostly RF systems. Heterojunction transistors have different semiconductors for elements of transistor. Usually emitter is composed of the larger bandgap material than the base. The figure describes that this difference in the bandgap allows the barrier for holes to inject backward into the base, denoted in the figure as Δφp, to be made large, while barrier for electrons to inject into base Δφn is made low. This barrier arrangement helps to reduce the minority carrier injection from base when the emitter-base junction is under the forward bias, and hence reduces base current and increases the emitter injection efficiency.
The improved injection of carriers into the base allows the base to have a higher doping level, resulting in lower resistance to access the base electrode. In the more traditional BJT, also referred to as homojunction BJT, the efficiency of carrier injection from the emitter to base is primarily determined by doping ratio between the emitter and base, which means that the base should be slightly doped to obtain high injection efficiency, making its resistance relatively high. Also higher doping in the base can improve the figures of merit like the Early voltage by lessening the base narrowing.
The grading of composition in the base, for instance, by progressively increasing the quantity of germanium in the SiGe transistor, causes a gradient in the bandgap in neutral base, denoted in figure by ΔφG, providing a "built-in" field which assists electron transport across the base. That drift component of the transport aids the normal diffusive transport, increasing frequency response of transistor by reducing the transit time across base.
Two frequently used HBTs are aluminum gallium arsenide and silicon-germanium, though a wide range of semiconductors can be used for HBT structure. HBT structures are usually grown by the epitaxy techniques such as MOCVD and MBE.
Email based Electronics Devices and circuits assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching Electronics Engineering assignment help expert for help with Heterojunction bipolar transistor questions? Heterojunction bipolar transistor topic is not easier to learn without any external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offers free lecture notes for Electronics Devices and circuits assignment help and Electronics Devices and circuits homework help. Live tutors are available 24x7 hours for helping students in their Heterojunction bipolar transistor related problems. We provide step by step Heterojunction bipolar transistor question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Heterojunction bipolar transistor topic under Electronics Devices and circuits theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving electronics engineering questions in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours