When some potential difference V is applied across a resistance R then the work done by the electric field on charge q to flow through the circuit in time t will be W=qV = Vit =V2t/4.2R Joule. This work seems as thermal energy in the resistor.
Heat produced by the resistance R is H = W/J = V2t/4.2R Cal. This relation is called joules heating.
Electric Power
The rate at which electrical energy is dissipated into other forms of energy is called electrical power i.e.
P = W/t = Vi =i2R=V2/R
Units: It's S.I. unit is Joule/sec or Watt
Bigger S.I. units are KW, MW and HP, remember 1 HP = 746 Watt
Rated values
On electrical appliances (Bulbs, Heater, Geyser ... etc). Wattage, voltage, ... etc. are shown named rated values e.g. If consider we have a light of 40 W, 220 V then rated power p=40 W while printed voltage V= 220V.
Resistance of electrical appliance
If variation of resistance with temperature is neglected then resistance of any electrical appliance can be calculated by rated power and rated voltage i.e. by using R=V2/PR
Power consumed (illumination)
An electrical appliance (Bulb, heater, ... etc.) consume rated power (PR) only if applied voltage (VA) is equal to rated voltage (VR) i.e. If VA = VR
So P = V2/R also we have R=V2/PR .
Long distance power transmission
When power is transmitted through a power line of resistance R, heat-loss will be i2R
Now if the power P is transmitted at voltage V then P = Vi , i.e. i = (P / V)
So Power loss = P2/V2*R
Now as for a given line and power, R and P are constant so Power loss
So if power is transferred at high voltage, power loss will be low and vice-versa. That is why long distance power retransmission is carried out at high voltage.
1. The price of electricity consumed is calculated on the basis of electrical energy and not on the basis of electrical power.
2. The unit Joule for energy is very small hence a big practical unit is considered known as kilowatt hour (KWH) or board of given unit (B.T.U.) or simple unit.
3. 1 KWH or 1 units is the quantity of electrical energy which dissipates in one hour in an electrical circuit when the electrical power in the circuit is 1 KW thus 3.6*108J.
4. Important formulae to determine the no. of used units is
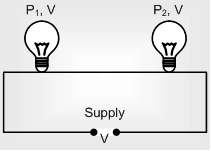
Series combination
|
(i) Total power consumed 1/Ptotal= 1/P1+1/P2...
(ii) If 'n' bulbs are identical, Ptotal= P/N
(iii) Pconumed ∝ V ∝ R ∝ 1/Prated i.e. in series combination bulb of lesser wattage will give more white light and p.d. seem across it will be more.
|
|
|
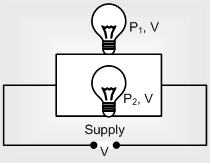
Parallel combination
(i) Total power consumed Ptotal= P1+P2..
(ii) If 'n' identical bulbs are in parallel Ptotal= nP
(iii) Pconumed ∝ 1/R ∝ Prated i.i.e. in parallel combination, bulb of larger wattage will give more white light and more current will pass through it.
|
|
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Heating & Chemical effect of Current questions? Heating & Chemical effect of Current topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Heating & Chemical effect of Current related problems. We provide step by step Heating & Chemical effect of Current question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Heating & Chemical effect of Current topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours