Gross Profit Ratio
The gross profit ratio measures the relationship of gross profit to net sales and is usually expressed as a percentage. Thus, it is calculated by dividing the gross profit by net sales.
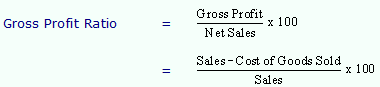
Cost of goods sold includes all the expenses relating to main trading activity of the business.
For Trading Concern
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Purchases + Direct Expenses - Closing Stock
For Manufacturing Concern
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock of finished goods + Cost of Manufacturing + Direct Expenses - Closing Stock of finished goods
For Software Services
Cost of goods sold = Costs relating to software development
Gross profit ratio represents the excess of what the concern is able to charge as sale price over the cost of goods sold. This surplus is available to meet the operating expenses and non-operating expenses. The amount remaining after meeting those expenses represents the net profit, which belongs to shareholders.
|
Gross Profit ratio is used by managers for analysis purposes. It indicates the extent to which selling prices of goods per unit may decline without resulting in losses on operations of a firm. It reflects the efficiency with which a firm manufactures its products. A high gross profit ratio indicates more income from the main business operations, which is desirable. A low gross profit ratio normally indicates high cost of goods due to unfavorable purchasing policies, lesser sales, lower selling prices, fierce competition, over-investment in plant and machinery, etc.
Managers also use gross profit margins for cost control purposes. In the case of trading industries, gross profit margins are used to determine inventory in interim statements, to estimate inventory in case of insured losses.
Auditors and Tax authorities use gross profit ratio to judge the accuracy of the accounting records.
|
Gross Profit Ratio of Infosys Technologies Ltd. for the years 2006-07 and 2005-06 is calculated in the following table. Infosys main business activity is software development. Thus, for calculating the gross profit ratio, only software related expenses and incomes should be taken into account.
(Rs. in crore)
|
|
2006-07
|
2005-06
|
|
Income from Software Services and Products (A)
|
13,149
|
9,028
|
|
Software Development Expenses (B)
|
7,278
|
4,887
|
|
Gross Profit (C = A - B)
|
5,871
|
4,141
|
|
Gross Profit Ratio (C) ¸ (A) x 100
|
44.64%
|
45.87%
|
Selling and distribution and general administration expenses are indirect expenses and should not be taken into account for determining the gross profit.
Gross profit ratio is slightly decreased. The year 2006-07 witnessed a growth rate of 45.65% in its income from software; however, a growth of 48.93% in software development expenses resulted in a decrease in Gross Profit. (Annual Report, Management Discussion Analysis).
Email based Accounting assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching Accounting expert for help with Gross Profit Ratio questions? Gross Profit Ratio topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Accounting assignment help and Accounting homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Gross Profit Ratio related problems. We provide step by step Gross Profit Ratio question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Gross Profit Ratio topic under Accounting theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving Accounting questions in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours