Graham's law of the diffusion and Effusion
(1) Diffusion is process of the spontaneous spreading and intermixing of gases to form the homogenous mixture irrespective of force of the gravity. While Effusion is the escape of the gas molecules through a tiny hole such as pinhole in a balloon.
· All the gases spontaneously diffuse into one another when they are brought into the contact of each other.
· Diffusion into the vacuum will take place quite more rapidly than diffusion into the other place.
· The rate of diffusion of a gas and its rate of effusion both depend on its molar mass. Lighter the gases diffuse faster than the heavier gases. The gas with highest rate of the diffusion is hydrogen.
(2) In accordance to this law, at the constant pressure and temperature, the rate of diffusion or effusion of the gas is inversely proportional to square root of its vapour density.
Thus, rate of diffusion 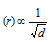 (T and P constant)
(T and P constant)
For the two or more gases at the constant pressure and temperature,
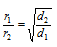
(3) Graham's law can be modified in several ways as,
(i) Since, 2 ´ vapour density (V.D.) = Molecular weight
then, 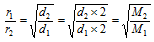
where, M1 and M2 are the molecular weights of the two gases.
(ii) Since, rate of diffusion (r)
= Volume of gas diffused/ Time taken for diffusion
then, 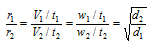
(a) When the equal volume of two gases diffuse that is V1 = V2
then, 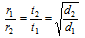
(b) When volumes of the two gases diffuse in almost the same time that is t1 = t2
then, 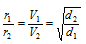
(iii) Since, 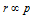 (when p is not constant)
(when p is not constant)
then, 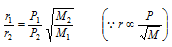
(4) The rate of diffusion and effusion can be determined as follows,
(i) The rate of diffusion is equal to the distance travelled by gas per unit time through the tube of uniform cross-section.
(ii) The number of moles effusing per unit time is also called as the rate of diffusion.
(iii) The decrease in pressure of the cylinder per unit time is called as rate of effusion of gas.
(iv) The volume of the gas effused through a given surface per unit time is also called as the rate of effusion.
(5) Applications : Graham's law has been used as as stated below,
(i) To determine the vapour densities and molecular weights of the gases.
(ii) To prepare the Ausell's marsh gas indicator, used in the mines.
(iii) Atmolysis : The course of separation of the two gases on the basis of their different rates of diffusion because of difference in their densities is called as atmolysis. It has been applied with the success for separation of isotopes and the other gaseous mixtures.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Graham's law of the diffusion and Effusion questions? Graham's law of the diffusion and Effusion topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Graham's law of the diffusion and Effusion related problems. We provide step by step Graham's law of the diffusion and Effusion question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Graham's law of the diffusion and Effusion topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours