Furnaces
In extraction of the metal different types of furnaces are taken in use. Each furnace has characteristics its own. Some principal furnaces have been described as follows,
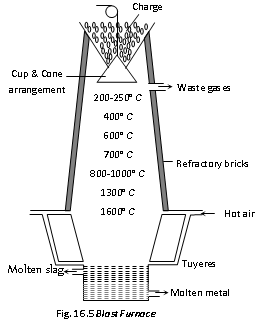
(1) Blast furnace : It is a special type of tall cylindrical furnace, about 100 feet high with the diameter of around15-28 feet. It is made of steel sheets lined inside with the fire-proof bricks. The charge is added through the cup and cone arrangement at top. At the upper part of furnace there is a hole for the passage of the waste gases of furnace. There are two outlets in hearth of furnace, one for tapping molten metal and the other above it for slag. The waste gases are heated and the hot air blast under pressure is blown into furnace by means of bellows or fans through the water cooled nozzles ortuyers. The temperature of the furnace ranges from 250oC. to 1500oC. Hence the charge descends slowly into the zone of increasing temperatures. The blast furnace is taken in use for the extraction of the metal such as copper and iron.
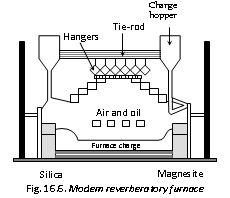
(2) Reverberatory Furnace: In the furnace fuel burns in a separate part and does not mix with charge. The furnace can be divided into 3 parts,
(i) Fire Grate : It is at one side where the fuel burns.
(ii) Flue or Chimney : It is at the other side of fire grate. The waste gases escape from it.
(iii) Hearth : It is the middle part of the furnace where the charge is heated with the flames and hot gases.
The material to be heated is placed on the hearth or bed of the furnace and is heated by the hot gases or flames produced by the burning of fuel. The waste gases leave out of the chimney. As the fuel does not come in contact with the charge, the furnace is very suitable for the calcination and roasting and is employed for oxidising and reducing both the purposes. For oxidation, the material is heated by the current of hot air while for reduction the material is mixed with coke and heated. The furnace finds the wide application in extractive metallurgy processes.
(3) Electric Furnace : The fuel burnt furnaces described hear produce temperature in the range of the temperature1000-1500oC. However these furnaces have the great utility in extraction of the metals yet these are not suitable where higher temperatures are required. One usually used electric furnace is Heroult's furnace shown in figure. It comprises of a steel shell lined inside with dolomite or magnesite. It gives movable water jacketed electrodes suspended from the roof or from the sides. Heat is obtained by striking an arc between the electrodes, thereby; a temperature of over 3000oC may be reached. The charge melts and the impurities such as Mn, Si, P and S etc. present in ore combine with basic lining to form slag, this is free from sulphur or the gas bubbles. Steel of quite fine quality is prepared by this method. The Electric furnaces are widely used where,
(i) Cheap power supply is available.
(ii) High temperature is required.
(iii) Pure product is needed.
As they find wide applications in a number of industries such as ceramices plastics chemical metallurgy, and also in the research laboratories. These furnaces are simply operated and has the problem of the storage of fuel and disposal of fuel waste.
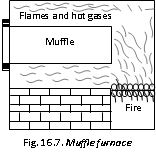
(4) Muffle Furnace : In this furnace the material to be heated does not come in the contact with the fuel or flames. This is a chamber made of refractory material and is surrounded by flames and hot gases on all sides. The products of the combustion process are removed through a door provided in the furnace. This furnace is used for the extraction of zinc, preparation of red lead, Pb3O4 and for testing the purity of precious metals like silver and gold. In an electric muffle furnace chamber is surrounded by the resistance coils.
(5) Bessemer Converter : A Bassemer converter is the pear-shaped 10 feet high, open at the top, lined with the refractory material like silica or magnesia which also acts as the flux. The converter is mounted on the trunnions, so that it can be tilted to collect products formed. There is an arrangement of introducing the hot blast of air from various small openings in the bottom of furnace. The converter is taken in use mostly for manufacturing of the copper of steel from pig iron. Passing the current of hot air into molten metal taken in the converter, the impurities are oxidised and leaves as gases or from slag. The Bessemer procedure is rapid one and does not take more than 15 minutes in production of one bath.
(6) Regenerative Furnace : These are furnaces in which the heat of the gases escaping out from the chimney is taken in use. Most of the furnaces particularly blast furnaces are fitted up with regenerated system which means an economy of the fuel. The flowing column of air is heated by hot flue gases, it is then brought again to the fire and returned to the furnace. This furnace is mainly used in the production of steel.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Furnace questions? Furnace topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Furnace related problems. We provide step by step Furnace question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Furnace topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours