Faraday's laws of electrolysis
The laws, which govern the deposition of substances (In the form of ions) on electrodes during the process of electrolysis, is known as Faraday's laws of electrolysis. These laws were given by Michael Faraday in the year1833.
(1) Faraday's first law : It states that,
"The mass of any substance deposited or liberated at any electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed. that isW is directly proportional to Q
Where,
W = Mass of ions liberated in gm,
Q= Quantity of the electricity passed in Coulombs
= Current in Amperes (I) × Time in second (t)
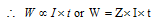
In case current efficiency (n) is given, then we can say that
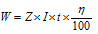
where, z=constant, known as electrochemical equivalent (ECE) of the ion deposited.
When a current of 1 Ampere is passed for 1 second (i.e.,Q=1), then, W=Z
Thus, electrochemical equivalent (ECE) may be defined as "the mass of the ion deposited by passing a current of one Ampere for one second (that is by passing Coulomb of electricity). It's unit is gram per coulomb.
Coulomb is the unit of the electrical charge.
96500 Coulombs = 6.023 * 1023 electrons = 1 mole electrons.
1 Coulomb = 6.023 * 1023/96500 = 6.28 * 1018 electrons,
or 1 electronic charge = 1.6 * 10-19 Coulomb.
(2) Faraday's second law : This law states that,
When the same amount of electricity is passed from different electrolytes, the masses of different ions liberated at the electrodes are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents (Equivalent weights).
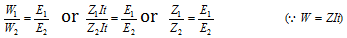
Thus the electrochemical equivalent (Z) of an element is directly proportional to its equivalent weight (E), i.e.,
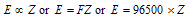
where, Faraday constant = 96500 C mol-1
So, 1 Faraday = 1F =Electrical charge carried out by one mole of electrons.
1F = Charge on the electron × Avogadro's number.
1F = e- * N = (1.602 * 10-19 c) * (6.023 * 1023 mol-1)
Number of Faraday = Number of electrons passed/6.023 * 1023
(3) Faraday's law for gaseous electrolytic product For the gases, we make use of the formula
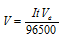
Here, V = Volume of gas evolved at STP at an electrode
Va = Equivalent volume = Volume of gas evolved at an electrode at STP by 1 Faraday charge
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Faraday's laws of electrolysis questions? Faraday's laws of electrolysis topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Faraday's laws of electrolysis related problems. We provide step by step Faraday's laws of electrolysis question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Faraday's laws of electrolysis topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours