The factors which influence heat of reaction: There are a number of factors which affect magnitude of the heat of reaction.
(i) Physical state of the reactants and products: Heat energy is involved for changing physical state of the chemical substance. For instance in conversion of the water into steam, the heat is absorbed and heat is given when steam is condensed. Taking the following two reactions
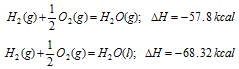
It is observed that there is difference in the value of ΔH if water is obtained in gaseous or liquid state. ΔH value in second case is higher because heat is evolved when steam condenses. Therefore, physical sate always affects the heat of reaction.
(ii) Allotropic forms of the element : Heat energy is also involved when one allotropic form of an element is converted into another. Thus, the value of ΔH depends on the allotropic form used in the reaction. For example, the value of ΔH is different when carbon in the form of diamond or in amorphous form is used.
C (diamond) 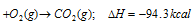
C (amorphous) 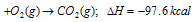
The difference between the two values is equal to the heat absorbed when 12g of diamond is converted into 12g of amorphous carbon. This is called as heat of transition.
(iii) Temperature : Heat of reaction has been found to depend upon the temperature at which reaction is occurring. The variation of heat of reaction with the temperature can be ascertained by making use of the Kirchhoff's equation.
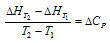
The Kirchhoff's equation at constant volume can be given as,
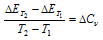
(iv) Reaction carried out at constant pressure or constant volume : When a chemical reaction occurs at constant volume, the heat change is known as the internal energy of reaction at constant volume. Though, most of the reactions are carried out at constant pressure; the enthalpy change is then termed as the enthalpy of reaction at constant pressure. The difference in values is negligible when the solids and liquids are involved in the chemical change. But, in reactions which involve the gases, the difference in two values is considerable.
Δ E+ Δ nRT= Δ H or qv+ Δ nRT=qp
Δ E=qv heat change at constant volume;
Δ H=qp heat change at constant pressure,
?n= the total number of moles of gaseous product-total number of moles of gaseous reactants
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with chemistry questions? Thermodyanmics topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Thermodyanmics related problems. We provide step by step Thermodyanmics question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Thermodyanmics topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours