Exceptional cases of evaluation of oxidation numbers : The rules described earlier are usually helpful in determination of the oxidation number of a specific atom in simple molecules but these rules fail in following cases. In this type of cases, oxidation numbers are evaluated using the concepts of chemical bonding involved.
Type I. In the molecules containing peroxide linkage in an addition to element-oxygen bonds. For example,
(i) Oxidation number of S in H2SO5
(Permonosulphuric acid or the Caro's acid)
By usual method; H2SO5
2*1+x+5*(-2)=0 or x = -8
But this cannot be factual as maximum oxidation number for S cannot exceed + 6. Since S has only 6 electrons in its valence shell. This exceptional value is due to the fact that two oxygen atoms in shows peroxide linkage as shown below,
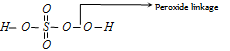
Thus the evaluation of o.n. of sulphur here should be made as follows,
2 × (+1) + x + 3 × (-2) + 2 × (-1)
(H) (S) (O) (O-O)
or 2 + x - 6 - 2 = 0 or x = + 6.
(ii) Oxidation number of S in H2S2O8
(Peroxidisulphuric acid or the Marshall's acid)
By usual method; H2S2O8
1 × 2 + 2x + 8 (-2) = 0
2x = + 16 - 2 = 14 or x = + 7
Type II. In molecules containing covalent and coordinate bonds, the below given rules are used for evaluating the oxidation numbers of atoms.
(i) For each of the covalent bond between dissimilar atoms the less electronegative element is assigned the oxidation number of + 1 while the atom of the more electronegative element is assigned the oxidation number of -1.
(ii) In case of the coordinate-covalent bond between similar or dissimilar atoms but donor atom is less electronegative than the acceptor atom, the oxidation number of +2 is assigned to the donor atom and an oxidation number of -2 is assigned to the acceptor atom.
Conversely, if the donor atom is more electronegative than the acceptor atom, contribution of the coordinate bond is neglected. The examples are as follows
(a) Oxidation number of C in 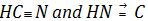
Evaluation of the oxidation number of C cannot be made directly by usual rules since no standard rule exists for oxidation numbers of N and C.
In such type of cases, evaluation of oxidation number should be made using indirect concept or by the original concepts of chemical bonding.
(b) Oxidation number of the carbon in 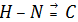 molecule
molecule
Contribution of the coordinate bond is neglected since the bond is directed from a more electronegative N atom (donor) to a less electronegative carbon atom (acceptor).
Therefore the oxidation number of N in 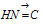 remains - 3 as it has three covalent bonds.
remains - 3 as it has three covalent bonds.
1 × (+ 1) + 1 × (- 3) + x = 0
H) (N) (C)
or 1 + x - 3 = 0 or x = + 2.
(c) Oxidation number of carbon in 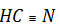
In 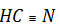 , N is more electronegative than carbon, each bond is gives an oxidation number of -1 to N. There are basically three covalent bonds; the oxidation number of N in
, N is more electronegative than carbon, each bond is gives an oxidation number of -1 to N. There are basically three covalent bonds; the oxidation number of N in 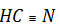 is taken as - 3
is taken as - 3
Now 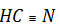 +1 + x - 3 = 0 x = + 2
+1 + x - 3 = 0 x = + 2
Type III. In a molecule containing two or more atoms of same or different elements in different oxidation states.
(i) Oxidation number of S in Na2S2O3
By usual method Na2S2O3
2 × (+1) + 2 × x + 3 (-2) = 0 or 2 + 2x - 6 = 0
or x = 2.
But this is unacceptable as the two sulphur atoms in Na2S2O3 cannot have the same oxidation number because on treatment with dil. H2SO4, one sulphur atom is precipitated while the other is oxidised to SO2.
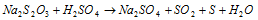
In this case, the oxidation number of sulphur is evaluated from concepts of chemical bonding. The chemical structure of Na2S2O3 is
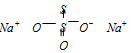
Because of the presence of a co-ordinate bond between two sulphur atoms, the acceptor sulphur atom has oxidation number of - 2 whereas the other S atom gets oxidation number of + 2.
2 × (+1) + 3 × (-2) + x × 1 + 1 × (- 2) = 0
( Na) (O) (S) (coordinated S)
or + 2 - 6 + x - 2 = 0 or x = + 6
Thus two sulphur atoms in Na2S2O3 have oxidation number of - 2 and +6.
(ii) Oxidation number of chlorine in CaOCl2
(bleaching powder)
In bleaching powder, Ca(OCl)Cl, the two Cl atoms are in different oxidation states i.e., one Cl- having oxidation number of -1 and the other as OCl- having oxidation number of +1.
(iii) Oxidation number of N in NH4NO3
By usual method N2H4O3 ; 2x + 4 × (+1) + 3 × (-1) = 0
2x + 4 - 3 = 0 or 2x = + 1 (wrong)
No doubt NH4NO3 has two nitrogen atoms but one N has negative oxidation number (attached to H) and the other has positive oxidation number (attached to O). Thus the evaluation should be made separately for NH4+ and NO3-
NH4+ x + 4 × (+1) = +1 or x = - 3
NO3- x + 3 (- 2) = -1 or x = + 5.
(iv) Oxidation number of Fe in Fe3O4
In Fe3O4, Fe atoms are in two different oxidation states. Fe3O4 can be considered as an equimolar mixture of FeO [iron (II) oxide] and Fe2O3 [iron (III) oxide]. Thus in one molecule of Fe3O4, two Fe atoms are in + 3 oxidation state and one Fe atom is in + 2 oxidation state.
(v) The Oxidation number of S in the sodium tetrathionate (Na2S4O6)
Its structure can be represented as follows,
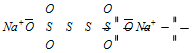
The two S-atoms which are linked to each other have oxidation number zero. Oxidation number of the other S-atoms can be calculated as shown below
Let oxidation number of S = x.
2 × x + 2 × 0 + 6 × ( - 2) = - 2
(For S) (For S-S) (For O)
x = + 5.
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Exceptional cases of oxidation numbers questions? Exceptional cases of oxidation numbers topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Exceptional cases of oxidation numbers related problems. We provide step by step Exceptional cases of oxidation numbers question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Exceptional cases of oxidation numbers topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours