Equilibrium Principles
A firm has to decide about the optimal output level. It will always try to choose that output level which provides maximum output at a given price and given point of time. The two ways to approach the problem are discussed here.
Total Revenue and Total Cost Approach
Comparison of the total revenue and total cost schedules can explain whether the firm is earning profits or incurring losses. Fig. 7.2 (a) shows that the profit of a perfectly competitive firm is maximum at output D, as the difference between TR and TC is maximum. The total revenue (TR) curve is a straight line from origin as the Market Structures IS; demand curve is perfectly elastic under perfect competition. Fig. 2.3 (chapter 2) depicts profit maximisation of a monopolist at output XIIm as difference between TR and Te is maximum at this output level. It should be noted that the total profit curve II is maximum at this level. The TR curve derives its shape from the downward sloping demand curve of a monopolist. Table A-1 and corresponding Fig A-1 in mathematical appendix show that profit is maximum when the difference between TR and TC is maximum.
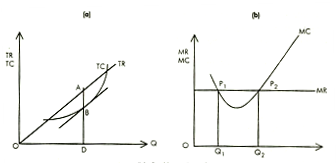
Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost Approach
The relation between marginal revenue and marginal cost determines the optimal output that should be produced by the firm. The profit-maximising rule states that a firm should produce output where the additional revenue received from the last
unit is equal to the additional cost of producing that unit. That is, MR = MC In Fig. 7.2 (b) the firm will increase output till point Q2' The firm will not choose point Q1 because the output is low and the marginal cost decreases with additional output. Therefore, at equilibrium point:
1. MC = MR and
2. The MC curve -should be increasing, i.e., intersect the MR curve from below.
It follows that the firm should raise output if MR > MC and reduce output if MR<MC
Both the approaches give same results. The profit maximisation theory explains in detail the two conditions for profit maximisation. Appendix 7 A gives a mathematical exposition of these conditions Marginal analysis will be used to determine optimal output in the rest of the chapter.
Firm and Industry Equilibrium
Market/industry equilibrium is determined by the intersection of the industry demand and supply. The corresponding output and price is the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price. Equilibrium of a firm differs from that of the industry under perfect competition as there are a large number of buyers and large sellers that establish the industry demand and supply as shown in Fig. 7.3. The firm has to sell at the price set by industry demand and supply forces. Under monopoly, the industry equilibrium coincides with firm equilibrium as there is a single seller in the market.
Managerial Economics Tutoring - Assignment Help
Our online managerial economics experts are here for your help. Expertsmind.com online assignment help-homework help brings you high grade in your courses and examination, We at Expertsmind.com offers managerial economics assignment help, managerial economics homework help and projects help. We offer complete package of managerial economics online tutoring for 24x7 hours.
ExpertsMind.com - Equilibrium Principles Assignment Help, Equilibrium Principles Homework Help, Equilibrium Principles Assignment Tutors, Equilibrium Principles Solutions, Equilibrium Principles Answers, Market Structures Assignment Tutors