Electrolytic conduction
When a voltage is applied to the electrodes dipped into an electrolytic solution, ions of electrolyte move and, thus, electric current flows throughout the electrolytic solution. The power of electrolytes to conduct electric current is termed as conductance or conductivity.
(1) Ohm's law : This law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it, i.e., I is directly proportional to V
where I is the current strength (In Amperes) and V is the potential difference applied across the conductor (In Volts)
or I=V/R or V=IR
where R is the constant of proportionality and is known as resistance of the conductor. It is expressed in Ohm's and is represented as the above equation is known as Ohm's law. Ohm's law can also be stated as,
The strength of the current flowing through the conductor is directly proportional to potential difference applied across the conductor and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
(2) Resistance: It measures the obstruction to the flow of current. The resistance of the specific conductor is directly proportional to the length (l) and inversely proportional to the area of cross-section (a) so that
Here 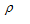 ( rho ) is the constant of proportionality and is called specific resistance or resistivity. The resistance depends on nature of the material.
( rho ) is the constant of proportionality and is called specific resistance or resistivity. The resistance depends on nature of the material.
Units : The unit of resistance is ohm 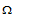 In terms of the SI unit, base unit is equal to (Kgm2)/(s3A2)
In terms of the SI unit, base unit is equal to (Kgm2)/(s3A2)
(3) Resistivity or specific resistance : We know that resistance R is 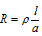 ; Now, if l = 1 cm, a = 1 cm2 then
; Now, if l = 1 cm, a = 1 cm2 then 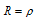
Thus, resistivity is defined as the resistance of a conductor of 1 cm length and having area of cross-section equal to 1 cm2
Units : The units of resistivity are 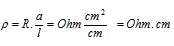
Its SI units are Ohm metre 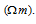 But quite often Ohm centimetre
But quite often Ohm centimetre 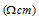 is also used.
is also used.
(4) Conductance : It is a measure of the ease with which current flows throughout the conductor. This is an additive property. It can be expressed as G. It is reciprocal of the resistance,
G=1/R
Units : The units of conductance are reciprocal Ohm (ohm-1) or mho. Ohm is also abbreviated as 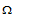 so that Ohm-1 may be written as
so that Ohm-1 may be written as 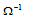
According to SI system, the units of electrical conductance is Siemens, S (i.e.,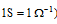
(5) Conductivity : The inverse of resistivity is called conductivity (or specific conductance). It is represented by the symbol, k (Greek kappa). The IUPAC has recommended the use of term conductivity over specific conductance. It can be defined as, conductance of a solution of 1 cm length and having 1 suare cm as area of the cross-section. Or we can say that conductivity is the conductance of one centimetre cube of a solution of an electrolyte.
Thus, 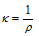
Units : The units of conductivity are 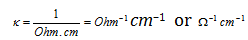
In SI units, l is expressed in m area of cross-section in m2 so that the units of conductivity are S m-1
(6) The Molar conductivity or the molar conductance : Molar conductivity can be defined as the conducting power of all the ions produced by dissolving one mole of an electrolyte in solution.
It is denoted by (λ). Molar conductance is related to specific conductance (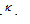 ) as,
) as,
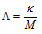
where, M is the molar concentration.
If M is in the units of molarity i.e., moles per litre (mol L-1) the λ may be expressed as,
For the solution containing 1 gm mole of electrolyte placed between two parallel electrodes of 1 sq. cm area of cross-section and one cm apart,
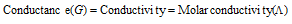
But if solution contains 1 gm mole of the electrolyte therefore, the measured conductance will be molar conductivity.
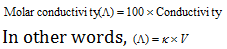
where V is the volume of solution in cm3 containing one gram mole of the electrolyte.
If M is the concentration of solution in the mole per litre,
M mole of electrolyte is present in the 1000cm3
1 mole of electrolyte is present in 1000/Mcm3 of solution
Thus, 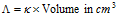 containing 1 mole of electrolyte.
containing 1 mole of electrolyte.
or 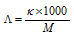
Units of Molar Conductance : The units of molar conductance can be derived from the formula ,
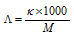
The units of Κ are S cm-1 and units λ of are,
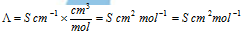
According to SI system, molar conductance is expressed as S m2 mol-1, if concentration is expressed as mol m-3.
(7) Equivalent conductivity : This can be defined as the conducting power of all the ions produced by dissolving one gram equivalent of an electrolyte in solution.
It is expressed as and is related to specific conductance as
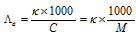 (M is Molarity of the solution)
(M is Molarity of the solution)
where C is the concentration in gram equivalent per litre (or Normality). This term has previously been quite frequently used. Now it is replaced by the molar conductance. The units of the equivalent conductance are ohm-1 cm2 (gm equiv)-1
(8) The Experimental measurement of conductance
(i) The conductance of the solution is reciprocal of its resistance, therefore, the experimental determination of the conductance of a solution involves the measurement of its resistance.
(ii) Calculation of conductivity : We have seen that conductivity (k) is reciprocal of resistivity (Ρ) ,

where G is the conductance of cell, l is the distance of the separation of two electrodes having cross section area a cm2
The quantity (1/a) is called cell constant and is expressed in cm-1 Knowing the value of cell constant and conductance of the solution, the specific conductance can be obtained as follows,
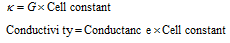
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Electrolytic conduction questions? Electrolytic conduction topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Electrolytic conduction related problems. We provide step by step Electrolytic conduction question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Electrolytic conduction topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours