A positive charge or a negative charge is said to create its field around itself. If a charge particle Q1 exerts a tension on charge Q2 placed near it, it may be stated that since Q2 is in the space of Q1, it finds some force, or it may also be said that since charge Q1 is inside the field of Q2, it experience some force. Thus space around a charge in which another charged particle experiences a force is said to have electrical field in it.
|
Electric field intensity: The electric field intensity at any point is defined as the force experienced by a unit positive charge placed at that point. 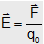
|

|
Where so the presence of this charge may not affect the source charge Q and its electric filed is not changed, therefore relation for electric field intensity can be better written as 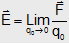
Unit and Dimensional formula: S.I. unit of relation-Newton /coulomb =volt/meter
and C.G.S. unit - Dyne/state coulomb.
Dimension:[E] = [MLT-3A-1]
Direction of electric field: Electric field (intensity) is a vector number. Electric field due to a positive particle is always away from the charge and that due to a negative charge is always towards the charge

Relation between electric force and electric field: In an electric field a charge (Q) experiences a force F = QE. If charge is positive then force is directed in the direction of field while if charge is negative force acts on it in the opposite direction of field

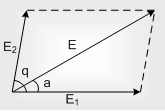
Super position of electric field: The given electric field and any point are equal to the vector sum of electric field fields at that point due to various charges.
|
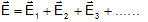
The value of the resultant of two electric fields is given by
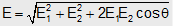
and the direction is given by
tanα = E2sinθ/E1+E2cosθ
|
|
Electric field due to regular distribution of charge: A system of closely spaced electric charges forms a continuous charge distribution
Continuous charge distribution
|
Linear charge distribution
|
Surface charge distribution
|
Volume charge distribution
|
|
In that kind of distribution charge distributed on a line.
|
In this distribution charge distributed on the surface.
|
In this distribution charge distributed in the whole volume of the body.
|
|
For example: charge on a wire, charge on a ring etc. Relevant parameter is λ which is called linear charge density i.e.,
|
For example: Charge on a conducting charged sphere, charge on a metal sheet etc. Relevant parameter is σ which is called surface charge density i.e.,
|
For example: Non conducting sphere. Related parameter is ρ which is called volume charge density i.e.,
|
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Electrical Field questions? Electrical Field topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Electrical Field related problems. We provide step by step Electrical Field question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Electrical Field topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours