|
General information: System of two same and reverse charges separated by a small fixed distance is called a dipole.
|
|
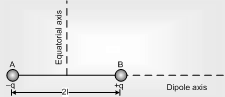
(i) Dipole axis: Line joining negative charge to positive charge of a dipole is called its axis. It may also be termed as its longitudinal axis.
(ii) Equatorial axis: Perpendicular sector of the dipole is known as it equatorial or transverse axis as it is perpendicular to length.
(iii) Dipole length: The displacement between two charges is known as dipole length (L = 2l)
(iv) Dipole moment: It is a quantity which gives information about the strength of dipole. It is a vector quantity and is directed from negative charge to positive charge along the axis. It is denoted as r and is defined as the product of the magnitude of either of the charge and the dipole length.
i.e. ρ = q(21)
Its S.I. unit is coulomb-metre or Debye (1 Debye = 3.3 * 10-30 C*m) and its dimensions are M0L1T1A1.
Dipole (electric/magnetic) in uniform field (electric/magnetic)
(i) Torque: If a dipole is placed in an uniform field such that dipole (i.e. or ) makes an angle q with direction of field then two equal and opposite force acting on dipole constitute a couple whose tendency is to rotate the dipole hence a torque is developed in it and dipole tries to align itself in the direction of field.
|
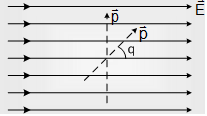
Consider an electric dipole in placed in an uniform electric field such that dipole (i.e. ) makes an angle q with the direction of electric field as shown
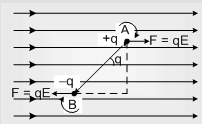
(a) Net force on electric dipole Fnet = 0
(b) Produced torque τ = ρEsinθ
|
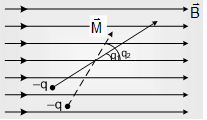
A magnetic dipole of magnetic field M is placed in uniform magnetic field B by making an angle q as shown
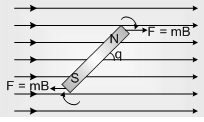
(a) Net force on magnetic dipole Fnet = 0
(b) torque τ = MBsinθ
|
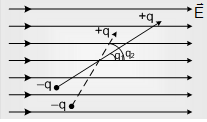
(ii) Work: From the above discussion it is clear that in an uniform electric/magnetic field dipole tries to align itself in the direction of electric field (i.e. equilibrium position). To change its angular position some work has to be done.
Suppose an electric/magnetic dipole is kept in an uniform electric/magnetic field by making an angle q1 with the movement, if it is again goes so that it makes an angle q2 with the field, work done in this process is given by the formula
|
|
|
|
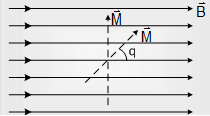
If and i.e. initially dipole is kept along the field then it turn through q so work done W=pE(1-cosθ)
|
If and then W = MB(1-cosθ)
|
(iii) Potential energy: In case of a dipole, potential energy of dipole is described as work done in rotating a dipole from a direction perpendicular to the field to the given direction i.e. if then -
|
W=U=pE(cos90-cosθ)
|
W=U=MB(cos90-cosθ)
|
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Electric Dipole questions? Electric Dipole topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Electric Dipole related problems. We provide step by step Electric Dipole question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Electric Dipole topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours