Discrete-time signals
A discrete-time signal can be represented as a sequence of numbers:

Here n is an integer, and x[n] is nth sample in sequence. The discrete-time signals are obtained by sampling continuous-time signals. In this case nth sample of sequence is equal to the value of the analogue signal xa(t) at time t = nT:

The sampling period is equal to T, and sampling frequency is fs = 1=T .
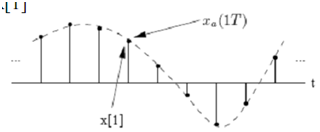
For this very reason, although x[n] is the nth number in the sequence, we refer to it as nth sample. We also refer to the sequence x[n]" when we mean the whole sequence. Discrete-time signals are depicted graphically as follows:
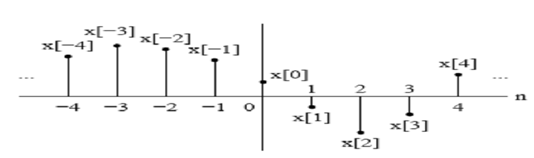
(This can be plotted by using MATLAB function stem.) The value x[n] is for noninteger values of n. The sequences can be manipulated in many ways. The sum and product of 2 sequences x[n] and y[n] are needed as the sample-by-sample sum and product respectively. Multiplication of x[n] by a is needed as the multiplication of every sample value by a. A sequence y[n] is a shifted or delayed version of x[n] if 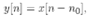
having n0 an integer.
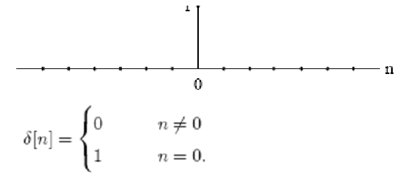
The unit sample sequence can be defined as
This sequence is referred to as a discrete-time impulse, or impulse. It plays the same role for the discrete-time signals as Dirac delta function does for the continuous-time signals. But, there are no mathematical complications in its definition.
A significant aspect of the impulse sequence is that an arbitrary sequence is represented as the sum of scaled, delayed impulses. For insyance, the
sequence is represented as follows
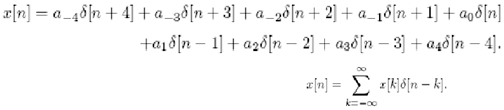
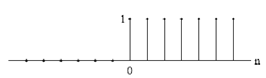
The unit step sequence can be defined as 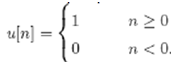
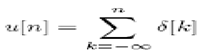
Alternatively, this can be expressed as
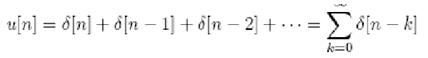
Conversely, unit sample sequence can be expressed as 1st backward difference of unit step sequence
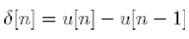
The exponential sequences are significant for analysing and representing discrete-time systems. The general form is 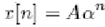
If A and B are real numbers then the sequence is real.
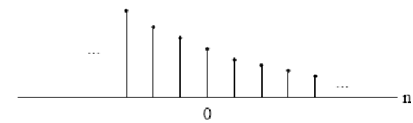
sequence changes in the sign, but decreases in the magnitude. For j_j > 1 the sequence grows in magnitude as the n increases. A sinusoidal 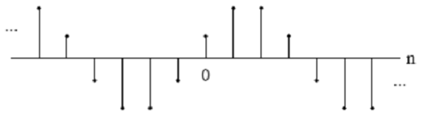
the sequence form 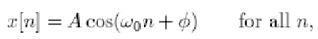
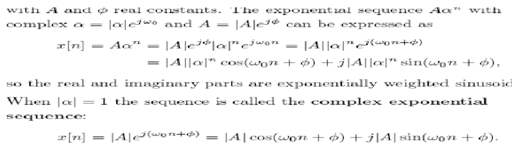
The frequency of this complex sinusoid is0, and can be measured in radians per sample. The index n is always an integer. This leads to some important differences between the properties of discrete-time and continuous-time complex exponentials: (ω0 + 2Π)
Consider complex exponential with frequency
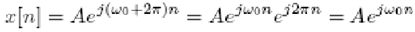
Therefore the sequence for complex exponential having frequency (ω0 + 2Π) is exactly the same as that for complex exponential with frequency. Generally, complex exponential sequences having frequencies(ω0 + 2Π) where r is an integer are indistinguishable from each other. Likewise, for sinusoidal sequences 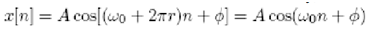
In continuous-time case, sinusoidal and complex exponential sequences are periodic. The discrete-time sequences are periodic (having period N) if x[n] = x[n + N] for all which requires that
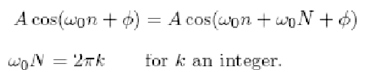
The same condition is needed for complex exponential sequence CejWonsequence to be periodic. The 2 factors described can be combined to reach the conclusion that there are N distinguishable frequencies only for which the corresponding sequences are periodic with the period N. One such set is given as follows
ωk = 2Πk/N, k = 0,1,2.....N-1
Email based Discrete-time signals assignment help - Discrete-time signals homework help at Expertsmind
Are you finding answers for Discrete-time signals based questions? Ask Discrete-time signals questions and get answers from qualified and experienced Digital signal processing tutors anytime from anywhere 24x7. We at www.expertsmind.com offer Discrete-time signals assignment help - Discrete-time signals homework help and Digital signal processing problem's solution with step by step procedure.
Why Expertsmind for Digital signal processing assignment help service
1. higher degree holder and experienced tutors
2. Punctuality and responsibility of work
3. Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
4. On Time Delivery
5. Privacy of information and details
6. Excellence in solving Digital signal processing queries in excels and word format.
7. Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours