Thermionic emission:
(i) The process of ejection of electrons from a metal surface by the application of heat is called thermionic emission and emitted electrons are called thermions and current flowing is called thermion current.
(ii) Thermions have different velocities.
(iii) This was discovered by Edison
(iv) Richardson - Dushman equation for current density (i.e. electric current emitted per unit area of metal surface) is given as 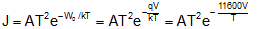
where A = emission constant = 12 * 104 amp/m2-K2 , k = Boltzmann's constant, T = Absolute temp and W0 = work function.
|
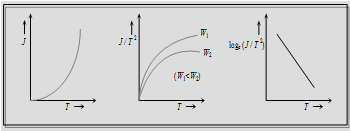
(v) The quantity of thermions emitted per second per unit area (J) depends upon following :
(a) J ∝ T2
(b) J ∝ e-w
|
|
Thermionic emitters: The emitters of electron are of two kinds
|
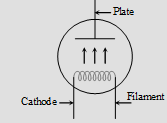
Directly heated emitter
|
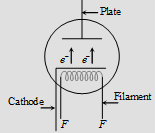
Indirectly heated emitter
|
|
|
|
|
(i) Cathode is directly heated by passing current.
|
(i) Cathode is indirectly heated.
|
|
(ii) Thermionic current is less.
|
(ii) Thermionic current is more.
|
|
(iii) Energy consumption and life is small.
|
(iii) Energy consumption and life is more.
|
Diode Valve
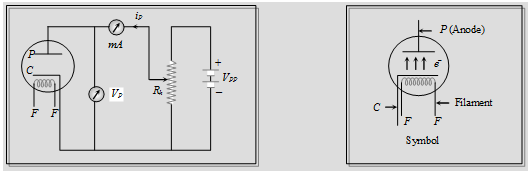
Working: When plate potential (vp) is positive, plate current (ip) flows in the circuit (because some emitted electrons reaches to plate). If + increases also increases and finally becomes maximum (saturation).
Space charge: If is zero or negative, then electrons collecting around the plate as a cloud which is called space charge. Space charge decreases the emission of electrons from the cathode.
|
Characteristic curve of a diode: A diagram shows the variation of with at a given filament current (ir) is known as characteristic curve.
The curve is not simple or linear hence diode valve is called as non-ohmic device.
|
|
(i) Space charge limited region (SCLR): In this region current is space charge limited current.
Also 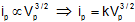
This is called child's law.
(ii) Linear region (LR) : ip ∝ vp
(iii) Saturated area or temperature limited region : In this part, the current is independent of potential difference applied between the cathode and anode.
ip = f(vp) ip=f (temperature)
The saturation current follows Richardson Dushman equation i.e. 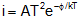
(iv) Diode resistance:
(a) Dc plate resistance or static plate resistance: Rp=vp/ip.
(b) Ac or dynamic plate resistance : If at fixed constant filament current, a small change ?VP in the plate potential produces a small change in the plate current, then the ratio ?VP/?ip is called the dynamic resistance, or the 'plate resistance' of the diode rp = ?VP/?ip .
Email based Physics assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching physics expert for help with Digital electronics questions? Digital electronics topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Physics assignment help and physics homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Digital electronics related problems. We provide step by step Digital electronics question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Digital electronics topic under physics theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving physics queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours