Determination of Molecular Mass : The molecular mass of the organic compounds can be determined by various methods.
(i) Physical methods for volatile compounds
(a) Victor Meyer's method : Molecular mass of volatile liquids and solids can be easily determined from the application of Avogadro hypothesis according to which the mass of 22.4 litres or 22400ml of the vapour of any volatile substance at NTP is equal to the molecular mass of the substance.
In Victor Meyer's method, a known mass of the volatile substance is vaporised in a Victor Meyer's tube. The vapours formed displace an equal volume of air into a graduated tube. The volume of air collected in graduated tube is measured under experimental conditions. This volume is converted to NTP conditions.
Calculations : Mass of the organic substance= Wg
Let the volume of the air displaced be =V1ml;
Temperature =T1K
Pressure (after deducting aqueous tension) =p1mm
Let the volume at NTP be=V2ml
Applying gas equation, 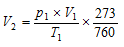
V2 ml of vapours weight at NTP = Wg
22400 ml of vapour weight at NTP 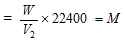
Alternate method: Vapour density of substance
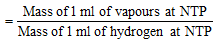
or V. D. = (W/V2)/0.00009 ( Mass of 1 ml of H2 at NTP = 0.00009 g or 2/22400)
or V. D. = W/(V2 * 0.00009) ;
Mol. Mass, 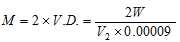
(b) Hofmann's method : The method is applied to those substances which are not stable at their boiling points, but which may be volatilised without decomposition under reduced pressure. A known mass of the substance is vaporised above a mercury column in a barometric tube and the volume of the vapour formed is recorded. It is then reduced to NTP conditions. The molecular mass of the organic substance can be calculated by the application of following relationship,
Mol. Mass 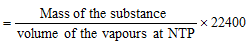
(ii) Physical methods for Non-volatile substances : The molecular mass of a non-volatile organic compound can be determined by noting either the elevation in boiling point of the solvent (Ebullioscopic method) or the depression in freezing point of the solvent (Cryoscopic method) produced by dissolving a definite mass of the substance in a known mass of the solvent. The molecular mass of the compound can be calculated from the following mathematical relationships :
(a) Elevation in boiling point :
Mol. Mass = 1000 Kb * w/ W * ΔT
Where, Kb = Molal elevation constant of the solvent, w = Mass of the compound, W= Mass of the solvent
ΔT = Elevation in boiling point of the solvent (determined experimentally)
(b) Depression in freezing point :
Mol. Mass = 1000 Kf * w/ W * ΔT
Where, Kf = Molal depression constant of the solvent, w = Mass of the compound, W=Mass of the solvent
ΔT = Depression in freezing point of the solvent (determined experimentally)
(iii) Chemical methods
(a) Silver salt method for acids : It is based on the fact that silver salt of an organic acid on heating gives residue of metallic silver.
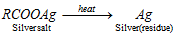
From the volume of the silver salt given and the mass of the silver residue obtained, the equivalent mass of the silver salt can be calculated.
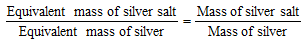
Knowing the equivalent mass of silver salt, the equivalent mass of the acid can be obtained. The molecular mass of an acid can be determined with the help of the following relationship,
Mol. mass of the acid = Equivalent mass of the acid * basicity
Calculations : (i) Mass of silver salt taken = wg (ii) Mass of metallic silver = xg
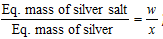 ; Eq. mass of silver salt = (w/x) * 108
; Eq. mass of silver salt = (w/x) * 108
Let the equivalent mass of the acid be E. In the preparation of silver salt, a hydrogen atom of the carboxylic group is replaced by a silver atom.
Thus, Equivalent mass of silver salt = E -1 + 108 = E + 107
Thus, E + 107 = (w/x) * 108 or E = [(w/x) * 108-107]
If n be the basicity of the acid, then Mol. Mass of the acid = [(w/x) * 108-107] * n
(b) Platinichloride method for bases : Organic bases combine with chloroplatinic acid, H2PtCl6 to form insoluble platinichlorides, which, on ignition, opt out a residue of metallic platinum. Knowing the mass of platinum salt and the mass of metallic platinum, the molecular mass of the platinum salt can be determined. Let B represents one molecule of the base. If the base is mono-acidic, the formula of the salt will be B2H2PtCl6.
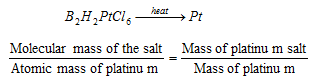
Let E be the equivalent mass volume of the base.
Molecular mass of the salt
= 2E +2 +195 +213 = 2E + 410
So 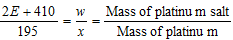 ;
;
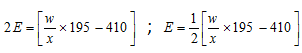
Mol. mass of the base = Eq. mass * acidity = E * n
where n is the acidity of the base.
(c) Volumetric method for acids and bases : Molecular mass of an acid can be determined by dissolving a known mass of the acid in water and titrating the solution against a standard solution of an alkali using phenolphthalein as an indicator. Knowing the volume of alkali solution used, the mass of the acid, which will require 1000 ml of a normal alkali solution for complete neutralisation can be calculated. This mass of the acid will be its equivalent mass.
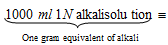 One gram equivalent of the acid
One gram equivalent of the acid
Calculations : Suppose w g of the organic acid requires V ml N1 alkali solution for complete neutralisation.
V ml N1 alkali solution = w gm acid
So 1000 ml N1 alkali solution = (w/V * N1) * 1000 g acid = one gram equivalent acid
Equivalent mass of the acid = (w/V * N1) * 1000
Thus, Molecular mass of the acid = Eq. mass * basicity
In the case of organic bases, the known mass of the base is titrated against a standard solution of an acid. Knowing the volume of the acid solution used, the mass of the organic base which will require 1000 ml of a normal acid solution for complete neutralisation can be calculated. This mass will be the equivalent mass of the base.
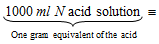 One gram equivalent of the base
One gram equivalent of the base
Molecular mass of the base = Eq. mass * acidity
Email based Chemistry assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching chemistry expert for help with Determination of Molecular Mass of Organic Compounds questions? Determination of Molecular Mass of Organic Compounds topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Chemistry assignment help and chemistry homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Determination of Molecular Mass of Organic Compounds related problems. We provide step by step Determination of Molecular Mass of Organic Compounds question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Determination of Molecular Mass of Organic Compounds topic under chemistry theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving chemistry queries in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours